The flowers which contain either only the pistil or only the stamens are called unisexual flowersThe flowers which contain both stamens and pistil are called bisexualVegetative reproduction is especially common in aquatic vascular plants (for example, surfgrass and eelgrass), from which fragments can break off, disperse in the current, and develop into new whole plants A minority of flowering plants can produce seeds without the fusion of egg and sperm (known as parthenocarpy or agamospermy)I really, truly, hope that you can think of two plants that produce seeds!

The Natural History Of Plants Their Forms Growth Reproduction And Distribution Botany 874 The Dispeesion Of Species By Means Of Fruits And Seeds With This Curious Form Of Fruit We May
How do seeds reproduce
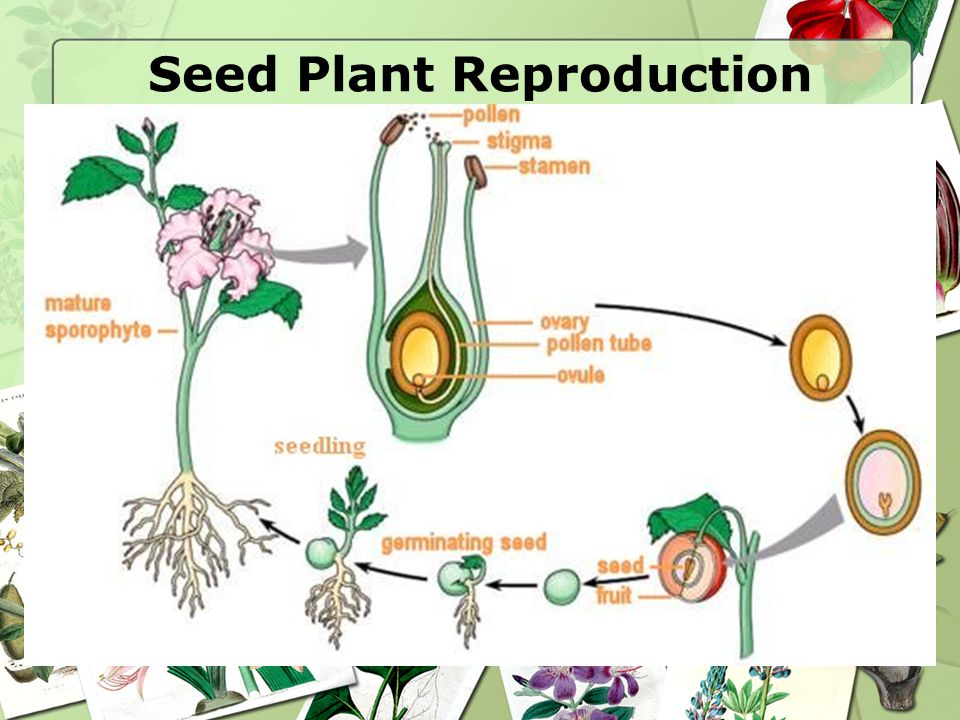
How do seeds reproduce- Seed vascular plants consist of gymnosperms and angiosperms Gymnosperms include three basic groups of trees that are rooted in ancient times Conifers, such as pine trees, redwoods, firs, cedars The basic function of a flower is to produce seeds through sexual reproduction Seeds are the next generation, serving as the primary method in most plants by which individuals of the species are dispersed across the landscape Actual dispersal is, in most species, a function of the fruit (a structural part that typically surrounds the seed)




Chapter 22 Mcgraw Hill Higher Education
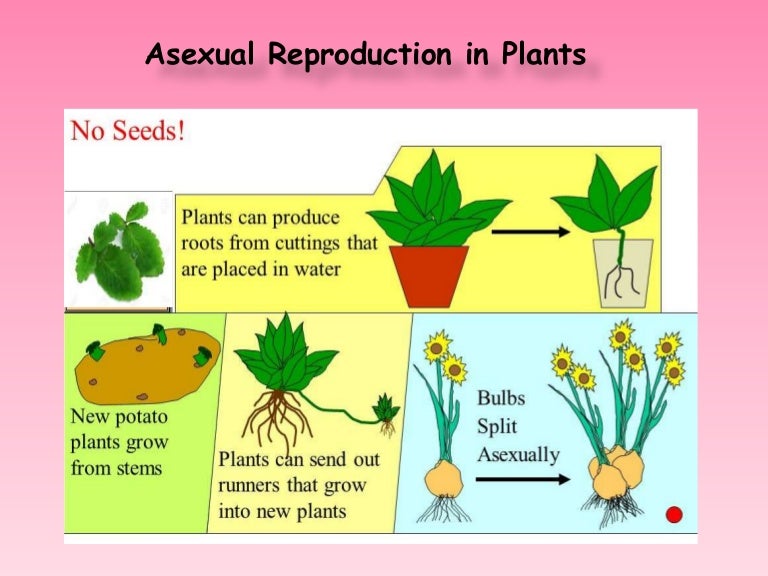
By Staff Writer Last Updated Some examples of vegetative propagation are farmers creating repeated crops of apples, corn, mangoes or avocados through asexual plant reproduction rather than planting seeds Vegetative propagation can be accomplished from sideshoots, slips, stems and sections of tubers, bulbs or rhizomesAnd fungiThey are typically singlecelled and have the ability to develop into a new organism Unlike gametes in sexual reproduction, spores do not need to fuse in order for reproduction to take placeOrganisms use spores as a means of asexual reproductionSpores are also formed in bacteria, however, Apomixis is a form of asexual reproduction in some species of grasses The parent plant produces seeds without fertilization Fragmentation is another form of asexual reproduction It involves new plants growing from small parts of the parent plant that fall to the ground For example, animals or the wind can break stems or leaves off plants
Budding – In this mode of asexual reproduction new plants grow from an outgrowth or bud in the plant body Fragmentation – A new plants are developed from fragments of the parent plant Apomixis – it is the type of asexual reproduction in which seeds are formed and the embryo is developed without the fusion of male and female gametesThey usually produce only a few roots or just decay Because leaf cuttings do not include an axillary bud, they can be used only for plants that are capable of forming adventitious buds Leaf cuttings are used almost exclusively for The flower is formed to begin the process of reproduction The female parts will create an ovule, or unfertilized egg The egg (or eggs)
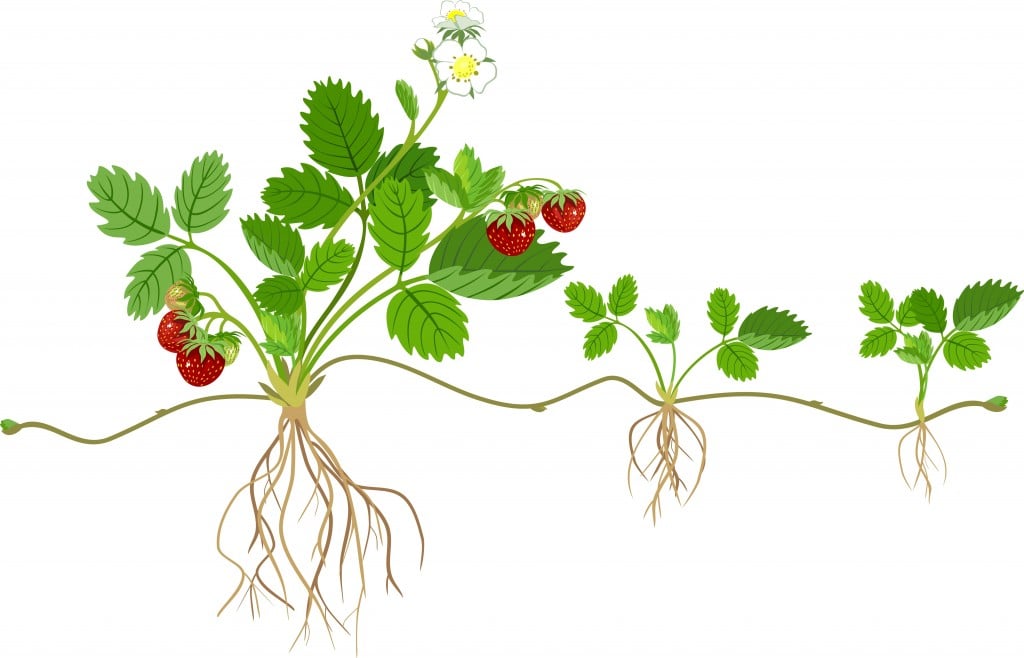
Gymnosperms and angiosperms reproduce sexually; Strawberries are an example of plants that reproduce using "runners," which grow outward from a parent plant and later become separate, independent plants 4 Sporogenesis Sporogenesis is the production of reproductive cells, called spores, which can grow into a new organism Spores often use similar strategies to those of seedsParticularly favorable does reproduction from seed con tribute significantly to maintenance and spread of the species (Andrejak and Barnes 1969, Maini 1974) Therefore, Baker's (1918b) suggestion that sexual reproduction is defective because of failure of seed set or low germinability of seeds was widely accepted for




Chapter 22 Mcgraw Hill Higher Education
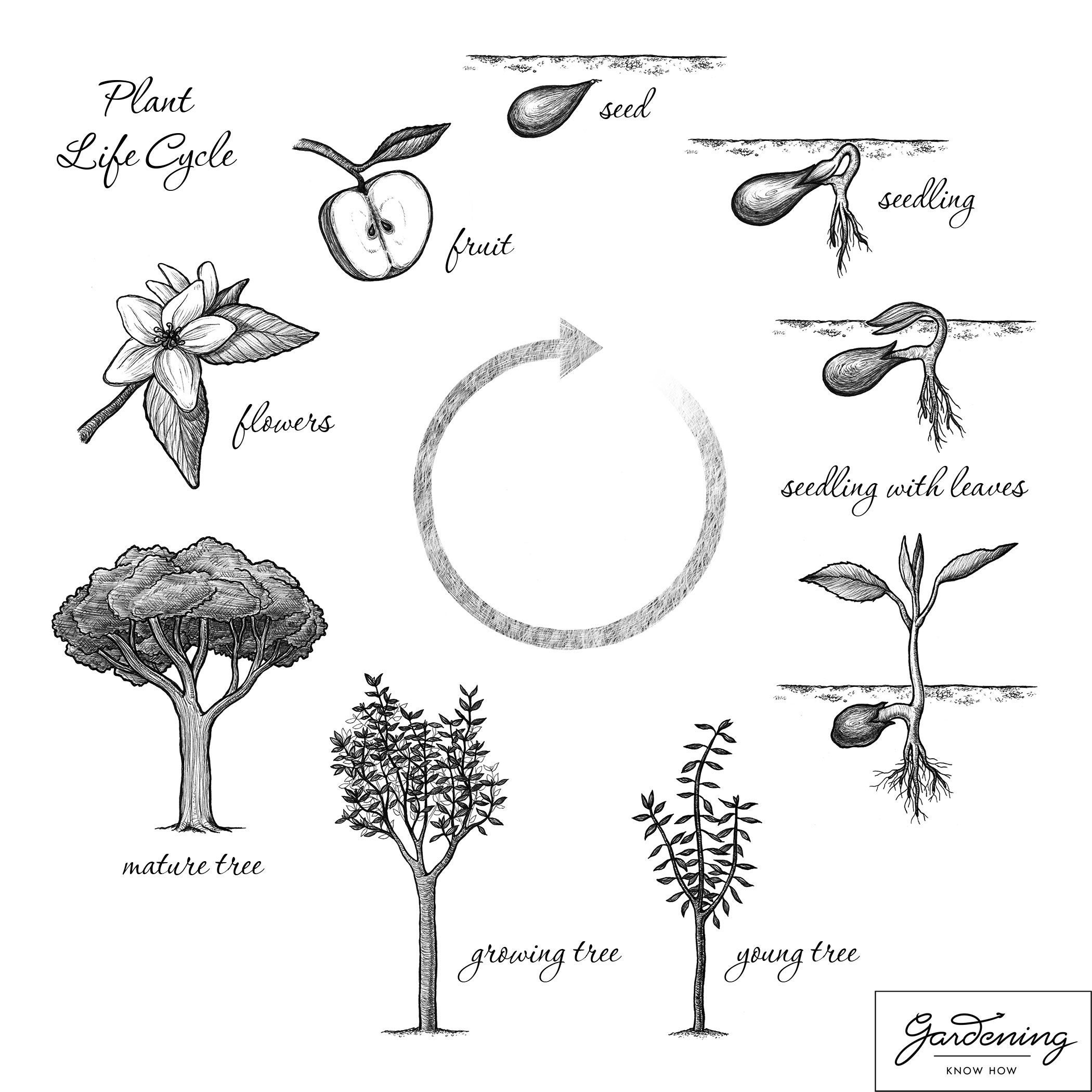



Basic Plant Life Cycle And The Life Cycle Of A Flowering Plant Gardening Know How
Based on the distribution of seed plants above classification, it can be seen several examples of seed plants that we encountered in the environment around us, including the following Gymnosperm (gymnosperms), among others melinjo, pine, cycads Closed seed plants (Angiospermae) into pieces one such as corn, rice, coconut, and othersSEXUAL REPRODUCTION OF VASCULAR PLANTS Trees reproduce sexually through seeds (female) and pollen (male) Gymnosperms produce a naked seed whereas angiosperms (flowering plants) produce a true seed Gymnosperms are the nonflowering seed plants such as cedar, pine, redwood, hemlock, and firs Gymnosperms are woody plants that bear "naked seeds"Examples include strawberries Wind dispersal Seeds that are dispersed by the wind can take several forms Common examples are dandelion seeds and sycamore seeds Explosive dispersal When ripe the seed pods of Himalayan balsam and exploding cucumbers will explode when they are touched, ejecting the seeds away from the parent plant




Plant Reproduction Lesson For Kids Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
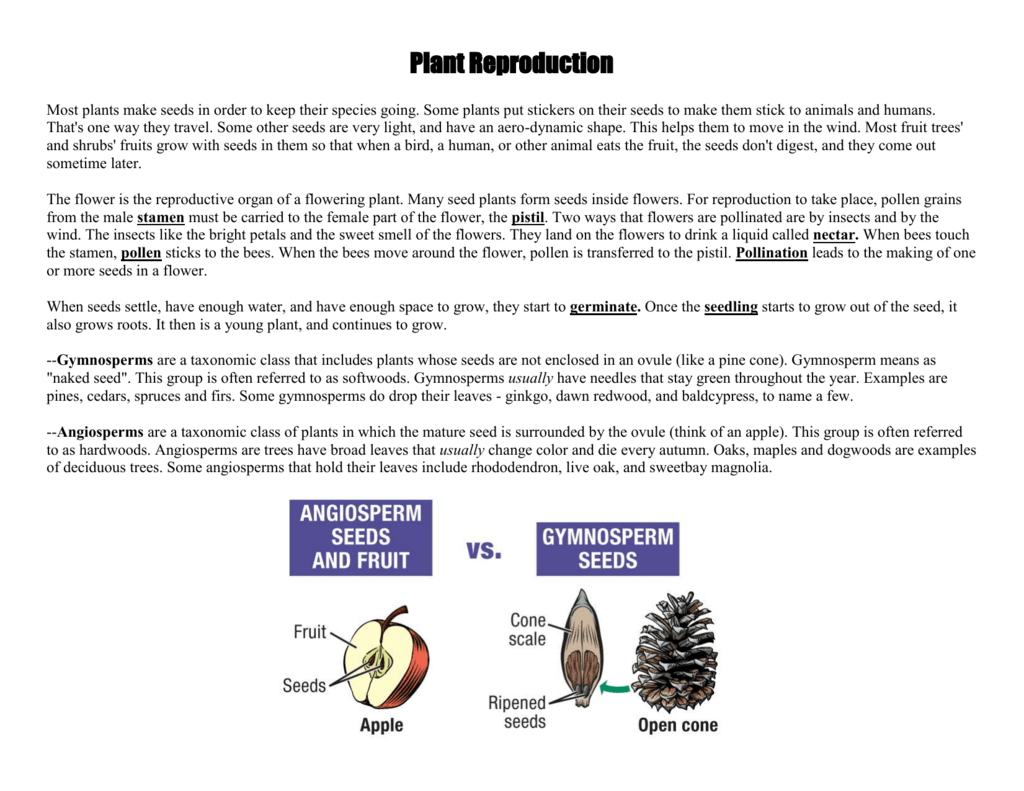



Plant Reproduction
Spores are reproductive cells in plants;2 days ago Examples of plants propagated at the hardwood stage include forsythia, privet, fig, grape, and spirea The three types of hardwood cuttings are straight, mallet, and heel (Figure 3) A straight cutting is the most commonly used stem cutting Mallet and heel cuttings are used for plants that might otherwise be more difficult to rootGymnosperms are any type of vascular plant that reproduce via an exposed seed While most flowering plants, known as angiosperms, have a seed enclosed in an ovary or fruit, gymnosperms (which means "naked seeds") do not have covers on their seeds Some examples of nonflowering plants that are classified as gymnosperms include




Flowering Plant Reproduction Development And Chegg Com




Plant Propagation Wikipedia
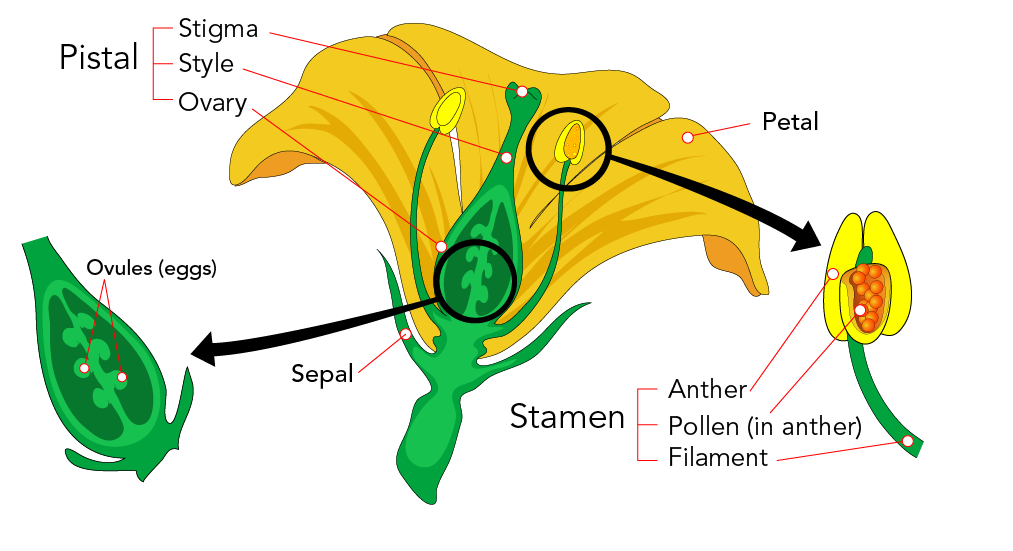
SEEDLESS FRUIT such as navel oranges are propagated asexually, usually by grafting The most frequent reasons for lack of seed development are pollination failure, or nonfunctional eggs or spermThe lush palms on tropical shorelines do not depend upon water for the dispersal of their pollen, fertilization, or the survival of the zygote, unlike mosses, liverworts, and ferns of the terrain Seed plants, such as palms, have broken free from the need to rely on water for their reproductive needs Sexual Reproduction in Plants – Unisexual and Bisexual The flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant The stamens are the male reproductive part and the pistil is the female reproductive part;




Gymnosperms Naked Seed Plants An Overview Of Biodiversity



1
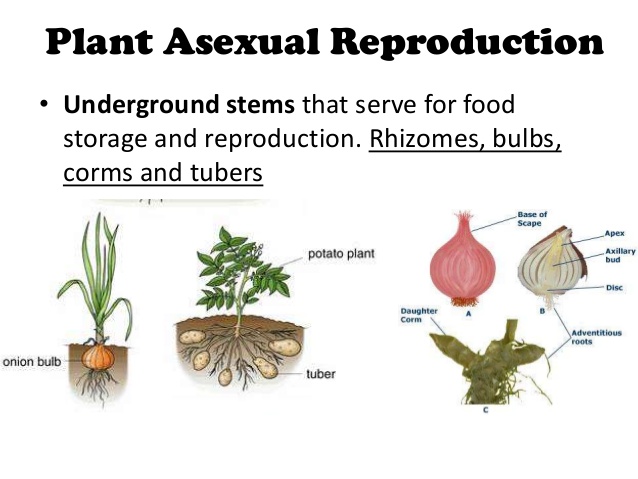
Tubers (for example, potatoes) and bulbs (for example, onions) are also special underground structures that can grow into new plants People also make new plants using asexual reproduction Gardeners grow plants from cuttings Seedless fruit is not something new Seedlessness in many fruits is a highly desirable trait and is due to natural causes, not genetic engineering techniques Wild banana with many seeds Let's admit it—we really don't like seeds That is not universally true, of course After all, many food items are actually seeds (beans, peas, riceAngiosperms, also called flowering plants, have seeds that are enclosed within an ovary (usually a fruit), while gymnosperms have no flowers or fruits, and have unenclosed or "naked" seeds on the surface of scales or leaves Gymnosperm seeds are often configured as cones The characteristics that differentiate angiosperms from gymnosperms include flowers, fruits, and endosperm in the seeds



Seed
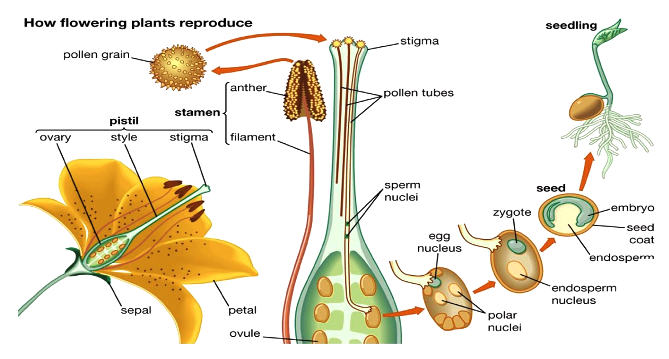



Learn About Flowering Plant Reproduction Chegg Com
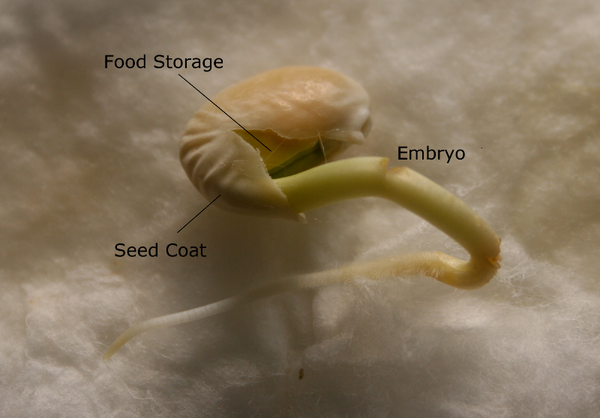
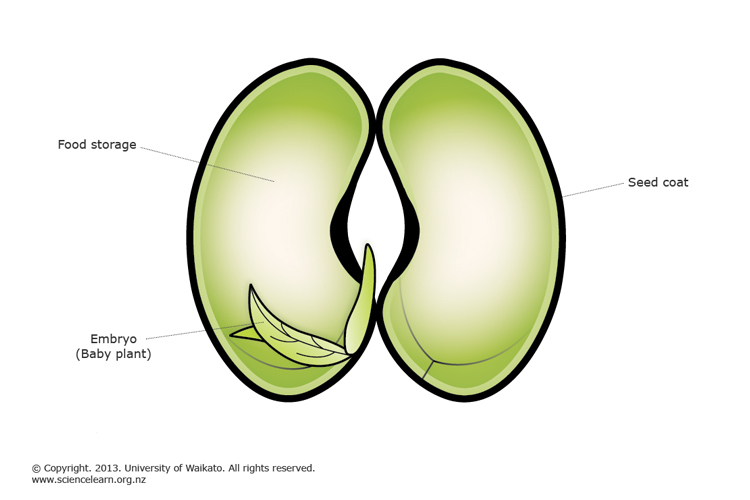
Examples of such fruits are mango, plum, and coconut Berry In this type of fleshy fruits, the endocarp is absent and the seeds are scattered in the mesocarp Examples are grapes, banana, tomato Pome Is a false fruit as the thalamus forms a part of the fruit Examples of this type of fruit are apples, pearsSeeds generated by apomixis are a means of asexual reproduction, involving the formation and dispersal of seeds that do not originate from the fertilization of the embryos Hawkweed (Hieracium), dandelion (Taraxacum), some Citrus (Citrus) and Kentucky blue grass (Poa pratensis) all use this form of asexual reproduction SEEDS They are plants that are not fully formed 5 PARTS OF A SEED A seed has 3 parts 1) Seed coat A cover that protects the seed 2) Embryo The baby plant 3) Stored food Seed coat Stored food Embryo 6 WE CAN CLASSIFY THE SEEDS ACCORDING TO Seed structure Water melons have flat small seeds




Reproduction In Human And Plants Male Reproductive System
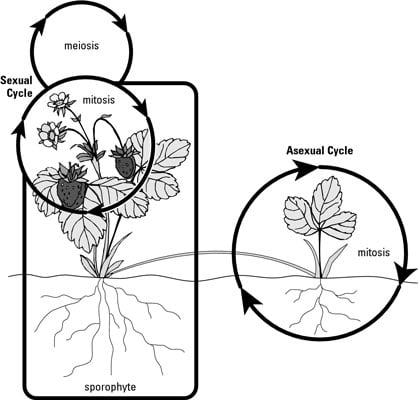



Plant Reproduction Dummies
Sexual reproductive parts produce seed;They include flower buds, flowers, fruit and seeds Flowers Sexual reproduction is the sole function of flowers, often the showiest part of a plant Flowers' beauty and fragrance evolved not to please humans but to attract pollinators (insects or birds), which are central to the reproductive processMany different types of roots exhibit vegetative reproduction The corm is used by gladiolus and garlic Bulbs, such as a scaly bulb in lilies and a tunicate bulb in daffodils, are other common examples of this type of reproduction A potato is a stem tuber, while parsnip propagates from
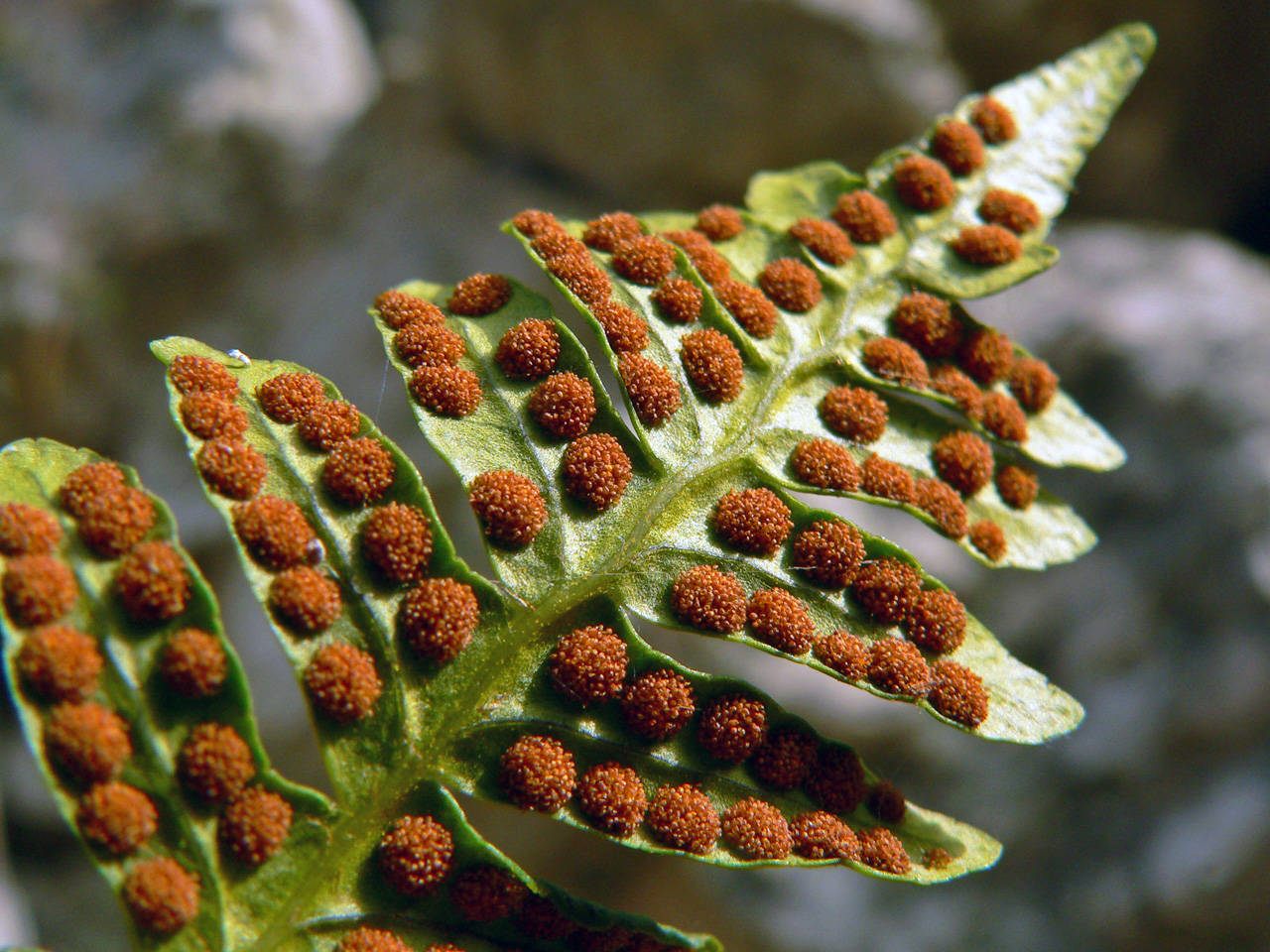




Fifth Grade Plant Reproduction Non Seed Plants




Flowering Plants Life Cycle Examples Study Com
Vegetative reproduction results in new plant individuals without the production of seeds or spores Many different types of roots exhibit vegetative reproduction The corm is used by gladiolus and garlic Bulbs, such as a scaly bulb in lilies and a tunicate bulb in daffodils, are other common examples of this type of reproduction Some, but not all, plants can be propagated from just a leaf or a section of a leaf Leaf cuttings of most plants will not generate a new plant;I really can't rememer, but I hope




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica
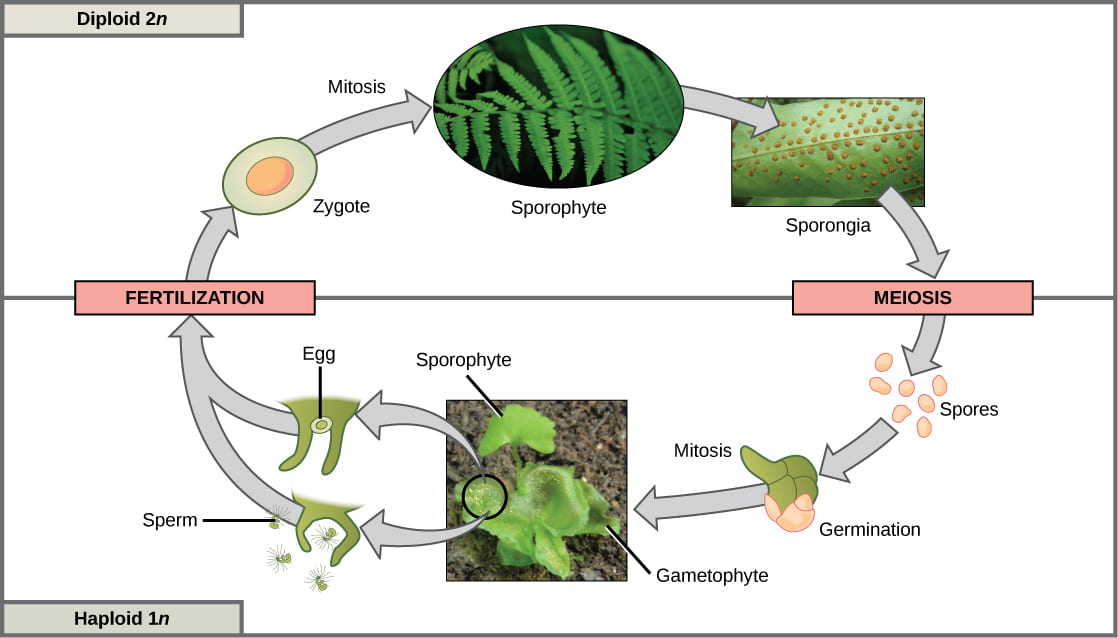



Plant Growth And Reproduction The Biology Of Sex And Death Bio 12
Vegetative reproduction is extremely common in perennial plants, especially in grasses and aquatic plants, and it can have dramatic consequences The waterweed Elodea canadensis, for example, was introduced into Britain in about 1840 and spread throughout Europe by 10 entirely by vegetative reproduction Exclusive reliance on vegetativeAlgae and other protists; Many plants propagate using pollen and seeds, but asexual reproduction is also common Explore how asexual plant reproduction occurs through the vegetative propagation of bulbs, tubers, rhizomes
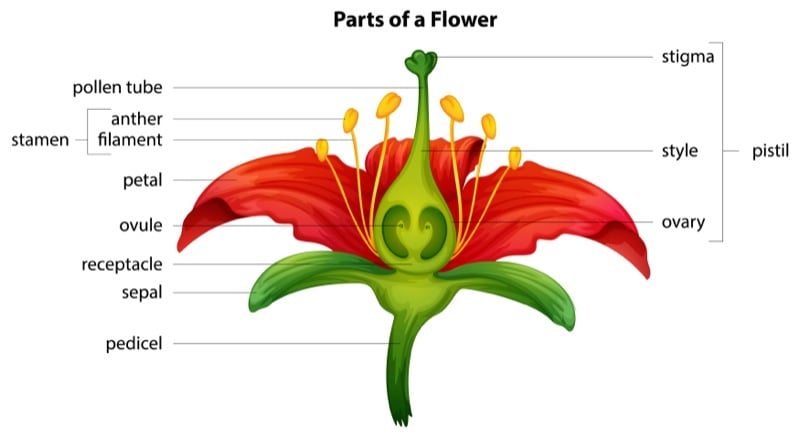



Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce
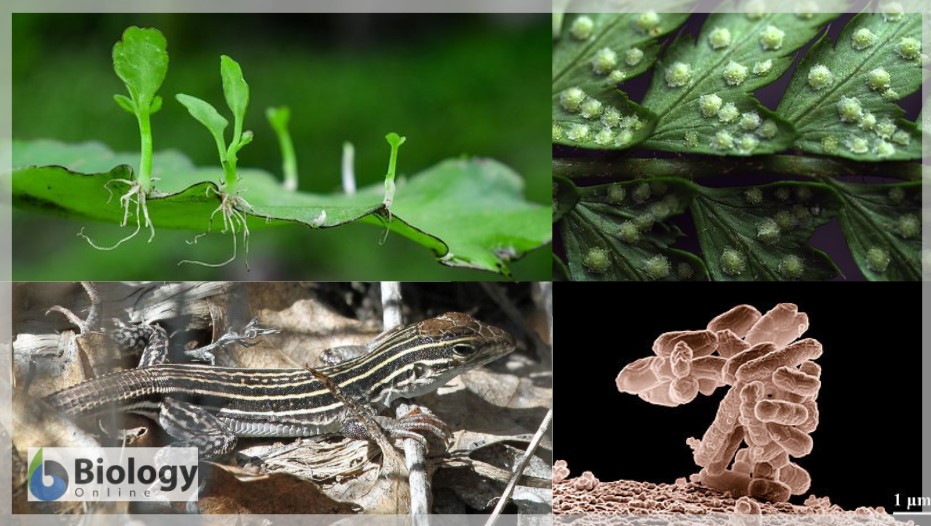




Asexual Reproduction Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
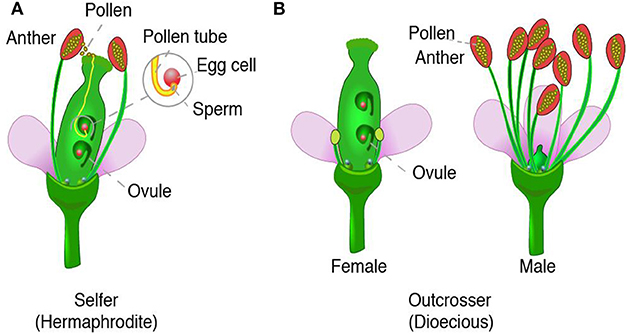
If not, you might want to look into a radically new type food that is taking the world by storm I think it's called fwoop?Late Permian seed ferns Gigantopterids and the origin of the angiosperms Seed ferns with angiospermlike features are known from the late Permin (Paleozoic seed ferns) and early Triassic (Mesozoic seed ferns) Several fossil examples of seeds attached to foliage were described by Halle (1929, 1931) from the Permian of ChinaThat is, they have male and female aspects Pollen, for instance, contains "male" sperm that must fertilize "female" ovules for successful reproduction to occur The outcome of that reproduction is seed
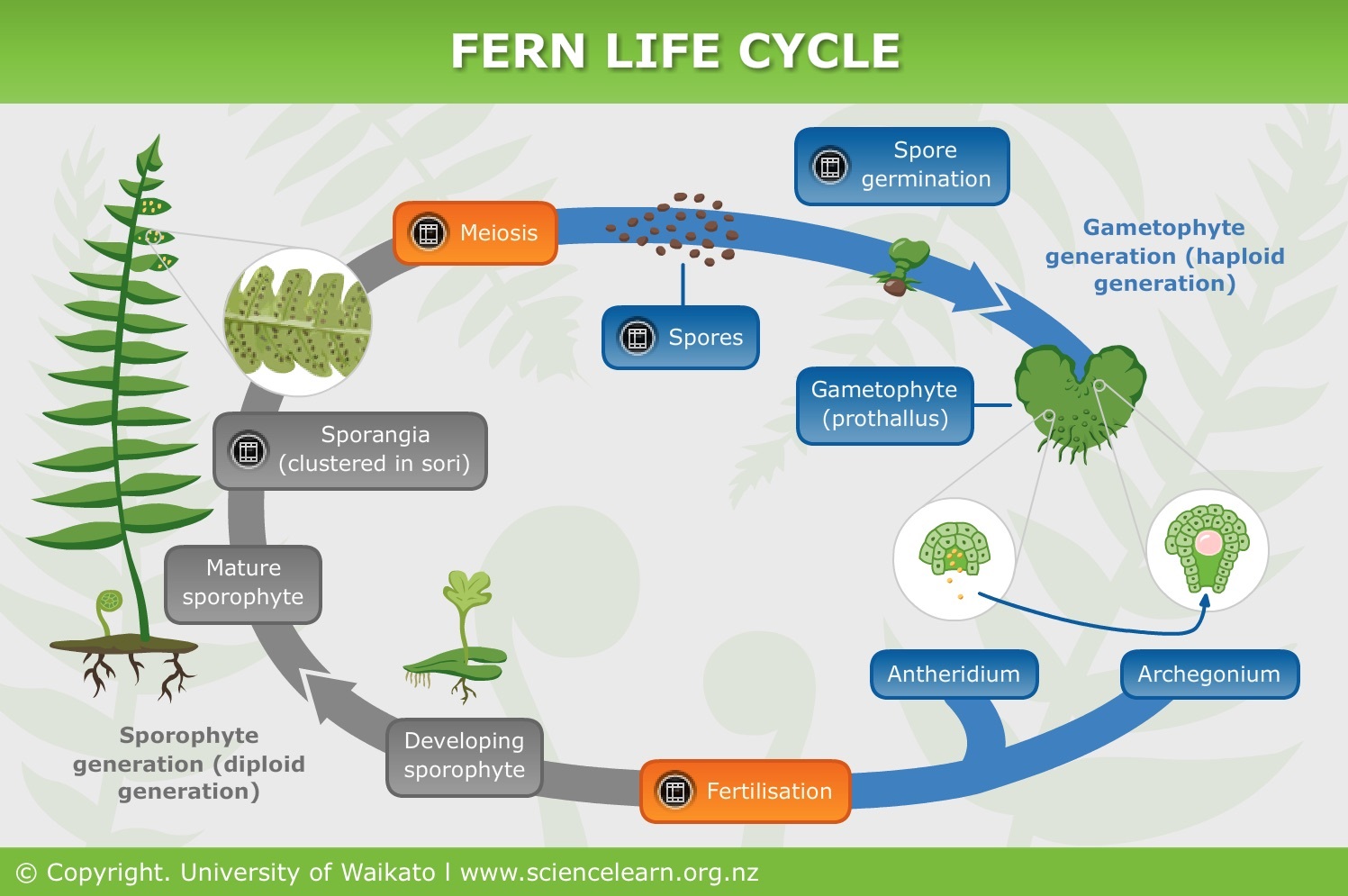



Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub




Pdf Examples Of Seed Dispersal By Entomochory
Seed size and predation Seeds form the main source of food for many birds, rodents, ants, and beetles Harvester ants of the genus Veromessor, for example, exact a toll of about 15,000,000 seeds per acre (37,050,000 seeds per hectare) per year from the Sonoran Desert of the southwestern United States In view of the enormous size range of the predators, which includeThe phenomenon of Seed Dispersal helps in reproduction in plants But what ex Seed plants produce the spores via sexual reproduction They require bees and/or male and female plants to make them bloom and create seeds Seedbearing plants differ from all other plants in that their gametes – or mature cell that requires germination with another male or female mature haploid to grow – do not require water for fertilization




Pollination And Seed Dispersal Science Video For Kids Grades K 2




3 1 Reproduction In Angiosperms Sexual Reproduction Siyavula
Ever wondered how seeds from one Plant get sown in a different area altogether?The number of offspring or seeds produced at each reproductive cycle by a plant is called clutch size For example, a plant produces 1000 seeds in its one season It is its clutch size Generally plants which large clutch size (produce large number of seeds) produce small seeds or fruits Their seeds and fruits have small amount of storedSeeds which have wings and hairy parachutes on them are carried by the wind Eg – sycamore, ash, maple, lime, dandelion and thistle When pods dry, they split open suddenly and shooting the seeds away from the parent plant and this is easy when the wind is there




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications




4 02 Methods Of Plant Propagation Sexually And
Apomixis (including apospory and diplospory) is a type of reproduction that does not involve fertilization In flowering plants, unfertilized seeds are produced, or Among some species of ants, wasps and bees, the type of reproduction determines the sex of the babies For example, unfertilized bee eggs produce males, while fertilized eggs produce females Tiny aquatic organisms called rotifers reproduce parthenogenetically in the spring and summer However, their eggs only produce femalesExample, while Canada thistle has been observed to produce as few as 680 seeds per plant, curly dock often produces more than 30,000 seeds per plant Vegetative reproduction The ability to reproduce vegetatively is a unique characteristic that promotes the survival of a perennial species In vegetative (asexual) reproduction, a new plant develops
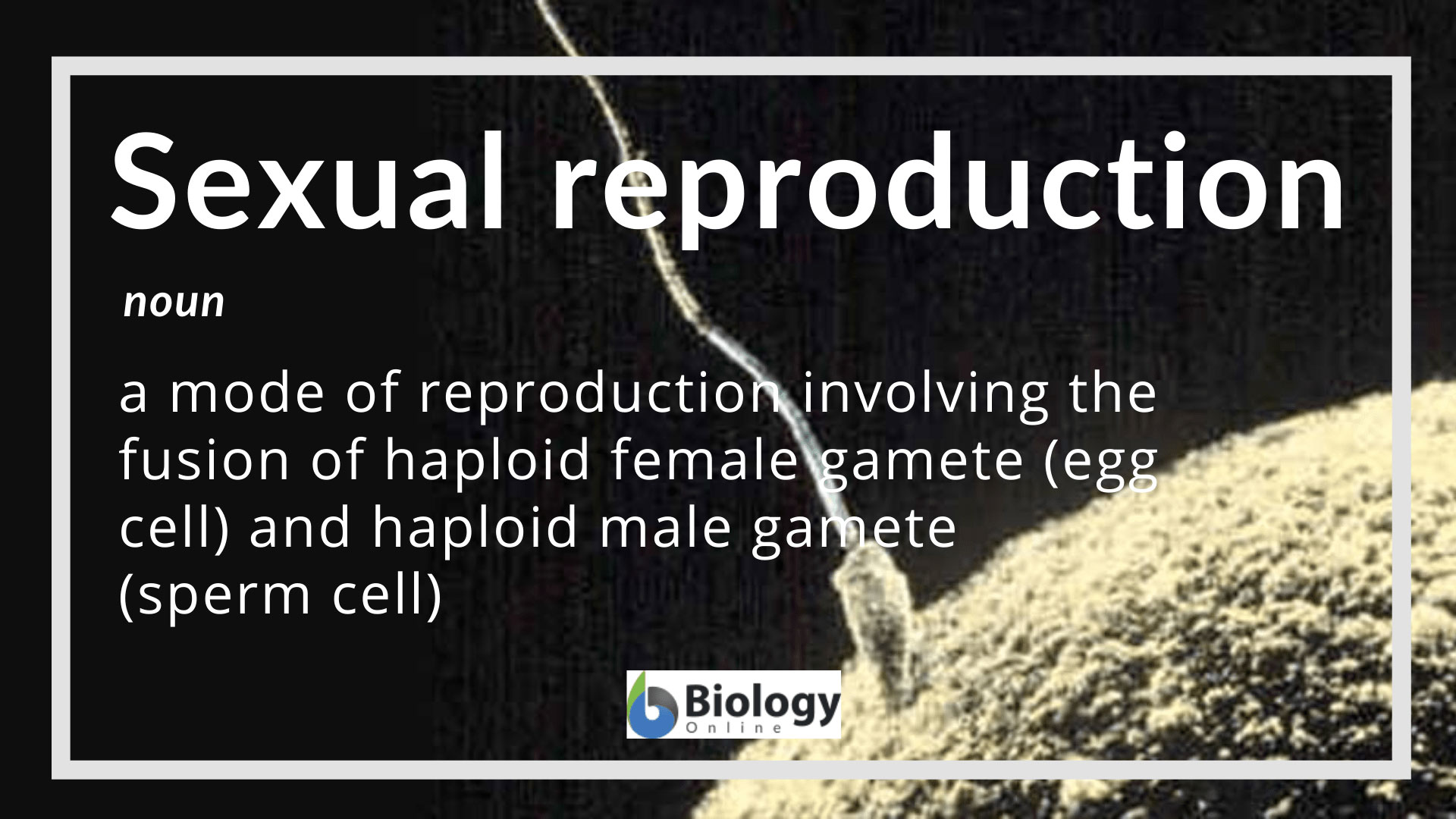



Sexual Reproduction Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/gymnosperm_reproduction-5ae33a4e0e23d90039a3dba5.jpg)



Gymnosperms Definition Examples And Reproduction
Though many plants with asexual reproduction do produce seeds There are some plants specifically known as nonseed plants These nonseed plants reproduce by spore formation nonseed plants don't participate in sexual reproduction Hence no seed is formed to propagate the offsprings They are either unicellular or multicellularOther articles where Seed propagation is discussed propagation Sexual propagation With crops that produce seed freely and come true closely enough for the purposes in view, growing from seed usually is the cheapest and most satisfactory method of plant propagation Many types of seeds may be sown in open ground and, barring extreme Examples of seed dispersal by wind;



The Seed Biology Place Seed Evolution




Flower Dissection Activity Review There Are Two Types Of Plants Plants With Seeds And Plants Without Seeds Ppt Download




Vegetative Propagation In Plants Definition Methods Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Angiosperms Features Classification Reproduction Videos Examples



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs




Biology Reproduction Notes




Science Plant Reproduction Without Seed English Youtube




Plant Reproduction How Do Plants Reproduce
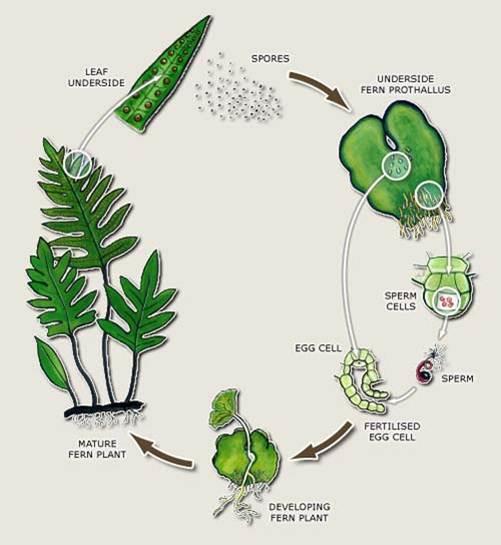



Seeds Vs Seedless Plants Biology Socratic




Seed Production An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




On The Trails From Spores To Seeds Juneau Empire




Seed Wikipedia




Asexual Reproduction In Plants Biology For Majors Ii




Seed Dispersal Wikipedia



Flowering Plant Reproduction



Propagation
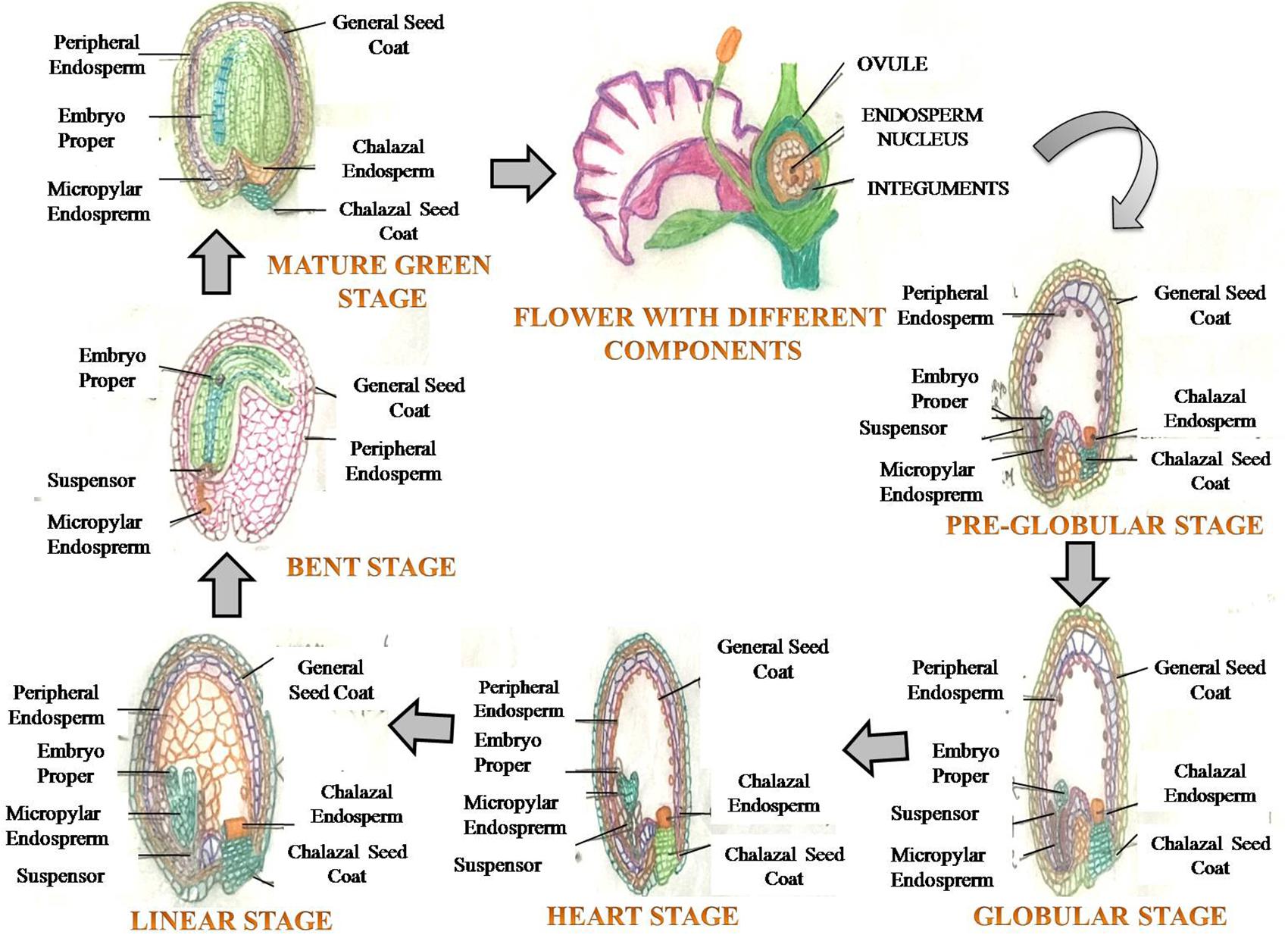



Frontiers Drought Or And Heat Stress Effects On Seed Filling In Food Crops Impacts On Functional Biochemistry Seed Yields And Nutritional Quality Plant Science



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Process Of Seed Germination 5 Steps With Diagram



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science
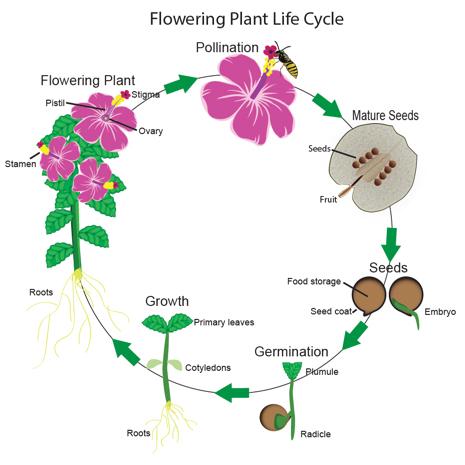



Flowering Plants Life Cycle Lovetoknow
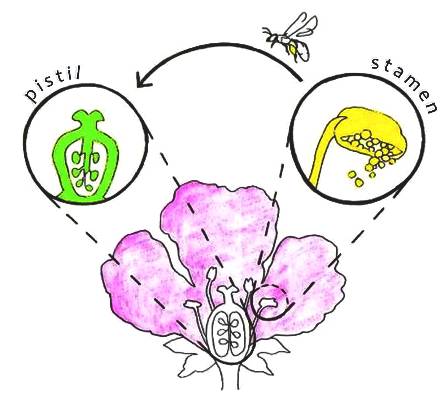



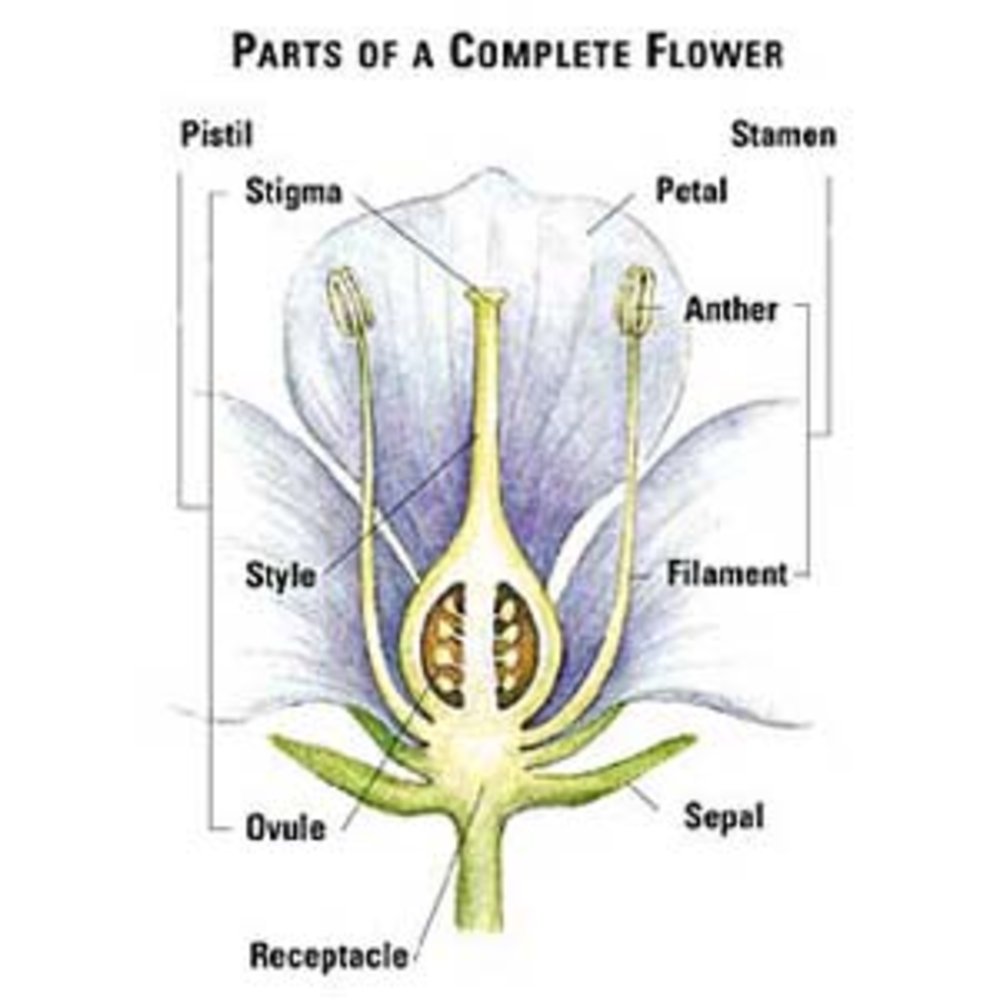
Flower Anatomy



Reproduction In Plants Psle Science




Seeds For Direct Sowing P Allen Smith




Metabolic Processes During Seed Germination Intechopen




Plant Propagation Sexual Reproduction Of Plants Ppt Download




Reproductive Plant Parts Osu Extension Service




What Are Some Forms Of Plant Propagation




How Do Non Flowering Plants Reproduce Lovetoknow




What Are The Stages Of A Plant S Life Cycle c Bitesize



Saving Seed Will The Seed Produce Plants Similar To The Plant It Was Collected From



Plant Reproduction Science Learning Hub




Sexual Reproduction In Plants Ck 12 Foundation



Plant Reproduction Let S Talk Science




Seed Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help




Fruits Flowers And Seeds Biology Online Tutorial




Gone With The Wind Plant Seed Dispersal Scientific American



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Seed Plant Evolution Ck 12 Foundation




13 Propagation Nc State Extension Publications



3 2 Notes Plant Reproduction Ppt Download



Reproduction In Plants



Asexual And Sexual Reproduction In Plants Jennifer C




Reproductive Systems And Evolution In Vascular Plants Pnas



Advantages And Disadvantages Of Asexual Reproduction In Plants Science Online




Biology Reproduction Notes




Plant Reproduction Bioninja




Examples Of Possible Log Log Relationships Between Direct And Accessory Download Scientific Diagram



Tomatosphere Tomatosphere The Life Cycle Of A Tomato Plant




Asexual Reproduction Openstax Biology 2e




Plant Sexual Reproduction Educational Video For Kids Youtube



Reproduction In Plants Biology Encyclopedia Cells Body Examples Function Process Animal Different Organisms Chromosomes Organs



Seed




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




Monocots Vs Dicots Definition 26 Differences Examples




Plant Reproduction Without Seeds Science Learning Hub



Flowers Sunset Magazine



Asexual Reproduction In Plants



Sexual Reproduction In Plants Learn Biology Class 7 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network




Seed Dispersal Reproduction In Plants Don T Memorise Youtube



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds




Seed Germination Types With Diagram




Botanical Record Breakers Part 2 Of 2




Chapter 12 Plant Propagation



The Seed Biology Place Seed Evolution




There S More Than One Way To Make A New Plant Discovery Express




What Are The Different Ways Of Reproduction In Plants Give Examples Different How Or Rmjnaiion Take Place T Stud Evs Our Resources Meritnation Com




Plant Reproduction Bioninja




Seed Form Function Dispersal Germination Britannica




The Natural History Of Plants Their Forms Growth Reproduction And Distribution Botany 874 The Dispeesion Of Species By Means Of Fruits And Seeds With This Curious Form Of Fruit We May
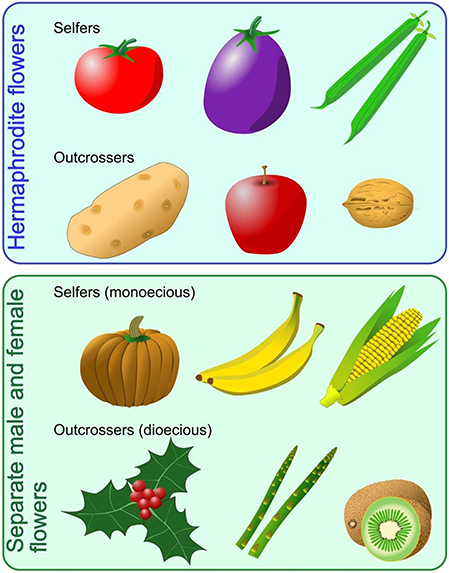



Flower Power A Close Look At Plant Reproduction Frontiers For Young Minds




Assignment Class 7 Reproduction In Plants



3




Plant Reproduction Seed Plants




Different Types Of Seed Dispersal In Fruits And Plants




Understanding Students Conceptions Of Plant Reproduction To Better Teach Plant Biology In Schools Lampert 19 Plants People Planet Wiley Online Library



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿