The odds ratio (OR) is a measure of how strongly an event is associated with exposure The odds ratio is a ratio of two sets of odds the odds of the event occurring in an exposed group versus the odds of the event occurring in a nonexposed group Odds ratios commonly are used to report casecontrol studies The odds ratio helps identify how likely an exposure is to lead to a specificAnd a risk of 095 is equivalent to odds of 19 Measures of effect for clinical trials with dichotomous outcomes involve comparing either risks or odds from two intervention groups To compare them we can look at their ratio (risk ratio or odds ratio) or their difference in risk (riskP = 2 3 implies 2 to 1 odds In this class, the odds ratio (OR) is the odds of disease among exposed individualsdivided by the oddsof diseaseamong unexposed OR = P(diseasejexposed)=(1 P(diseasejexposed))
27 Sep 01 Draft
What is the difference between odds ratio and risk ratio
What is the difference between odds ratio and risk ratio-May 18, 12 · Examples of measures of association include risk ratio (relative risk), rate ratio, odds ratio, and proportionate mortality ratio Risk ratio Definition of risk ratio A risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another groupTherefore, the importance of risk ratios depends upon the baseline risk



Solved Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Rati Chegg Com
Jul 01, 17 · After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 14 (mortality is 14 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium) Because the incidence rate in the nondelirium group is high, the odds ratio exaggerates the true risk demonstrated in the studyNov , 18 · To the Editor Dr Norton and colleagues 1 described significant limitations of odds ratios (ORs) but they did not report one important advantage of ORs compared with risk ratios (RRs) the magnitude of the association between an exposure and a dichotomous outcome is invariant to whether the outcome is defined as event occurrence (eg, death) or nonoccurrenceFigures etc Figure 1 Probability (P) vs Odds (O) where p=probability of success and q=probability of failure
Sep 02, · The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equalThe odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studiesE) But what about the Odds ratio?
R C = absolute risk in the unexposed group, given as a fraction (for example fill in 10% risk as 01) Confusion and exaggeration Odds ratios have often been confused with relative risk in medical literatureFeb 01, 08 · Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeableAug 07, 14 · If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different concept The odds indicates how much more likely is an event to occur than not to occur (p/(1p))



When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
Oct 07, 11 · Definition The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed) Example I often think food poisoning is a good scenario to consider when interpretting ORs Imagine a group of friends went out toRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the odds ratioIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals
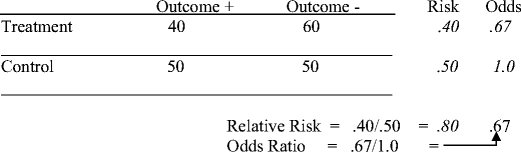
A value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalMay 04, 09 · A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence intervals 26 , 32 ,The probability of PONV with no Drug X is 40/100 or 040 Therefore, the relative risk for PONV with Drug X vs PONV without Drug X is 0/040 = 05 Odds ratios are used instead of relative risk for casecontrol studies To be able to calculate relative risk, we compare the risks of outcome in different groups



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table
Ref=reference category Table A PORs are reciprocals of each other and pvalues are the same regardless of which outcome (yes or no) is modelledFeb 21, 19 · On the other hand, if the risk in the unexposed group is 005, but the risk in the exposed group is 025, you still have a risk ratio of 5 But the risk difference is now 02!Dec 30, 16 · CI=confidence interval;



Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf



How To Calculate Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Google Search
May 15, 14 · The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/(c/d) = (ad)/(bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers RR = (a/(ab))/(c/(cd)) = (a(cd))/(c(ab))One of the most commonly observational study designs employed in veterinary is the crosssectional study with binary outcomes To measure an association with exposure, the use of prevalence ratios (PR) or odds ratios (OR) are possible In human epidemiology, much has been discussed about the use ofAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% =



Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To
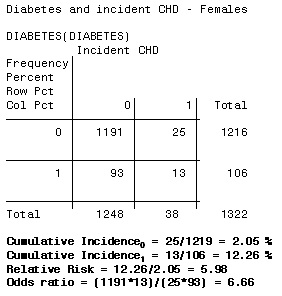


3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507
To understand what an odds ratio means in terms of changes in numbers of events it is simplest to first convert it into a risk ratio, and then interpret the risk ratio in the context of a typical control group risk, as outlined above The formula for converting an odds ratio to a risk ratio is provided in Chapter 12 (SectionOdds ratio and relative riskOdds Ratios (ORs) Allele Counting Cases Controls T A B C C D OR T = 1 implies no association between genotype and disease OR T >1 implies that the T allele is associated with the disease OR T



Glossary Of Research Terminology



Table 1 From When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RRJan 04, 19 · Reviewed and revised 26 August 15 OVERVIEW An odds ratio (OR) is a measure of association between an exposure and an outcome The OR represents the odds that an outcome will occur given a particular exposure, compared to the odds of the outcome occurring in the absence of that exposureIn practice the odds ratio is commonly used for casecontrol studies, as the relative risk cannot be estimated In fact, the odds ratio has much more common use in statistics, since logistic regression, often associated with clinical trials, works with the log of the odds ratio, not relative risk Because the (natural log of the) odds of a


Case Control Study Odds Ratio Relative Risk Best Custom Academic Essay Writing Help Writing Services Uk Online Homeworknowcomlink Web Fc2 Com



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
Mar 19, 18 · The relative risk (or risk ratio) is an intuitive way to compare the risks for the two groups Simply divide the cumulative incidence in exposed group by the cumulative incidence in the unexposed group where CI e is the cumulative incidence in the 'exposed' group and CI u is the cumulative incidence in the 'unexposed' groupFor example, a risk of 05 is equivalent to an odds of 1;The magnitude of the odds ratio is called the "strength of the association" The further away an odds ratio is from 10, the more likely it is that the relationship between the exposure and the disease is causal For example, an odds ratio of 12 is above 10, but is not a strong association An odds ratio of 10 suggests a stronger association



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios


Solved Week 6 Homework 1 Calculate A Relative Risk Factor Risk Ratio For The Below Problem Use The Numbers Given To You Below And Base Calcu Course Hero
Rather the odds is threefold greater Interpretation of an OR must be in terms of odds, notOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)Jan 10, 13 · Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect size


44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 Review 1 Similar To The Risk Ratio Here Are The Guidelines For Calculating A Confidence Interval For 2 Independent Samples And The Odds Ratio As The Parameter Of Interest 2 Note That Calculation Of The Confidence



Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
Apr 21, 21 · Risk ratio RR = CI e /CI u where CI e =cumulative incidence in exposed (index) group and CI u = cumulative incidence in the unexposed (reference) group Odds ratio OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in unexposed) Both RR and OR are estimates from samples, and they are continuous measuresRR = relative risk;OR = odds ratio;



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



In A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Estimates From Observational Studies Can I Pool Or With Hr And Rr Probably Not How Can I Transform Hr To Or
Jul 11, 16 · The ratio of these two probabilities R1/R2 is the relative risk or risk ratio Pretty intuitive If the program worked, the relative risk should be smaller than one, since the risk of failing should be smaller in the tutored group If the relative risk is 1, the tutoring made no difference at allThe Odds ratio is 14 x 9,999 Odds ratio = = 14 1 x 9,986 (this is a shortcut formula, only usable in 2x2 tables = n11×n22 n12×n21 where n11 is the upper left, n12 the upper right, etc) almost the same (it is the same if you round it like here) But now a little mathematical factOdds ratio Another measure of association is the odds ratio (OR) The formula for the OR is The odds ratio is used in place of the risk ratio or rate ratio in casecontrol studies In this type of study, the underlying population at risk for developing the health outcome or disease cannot be determined because



Measuring Of Risk



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
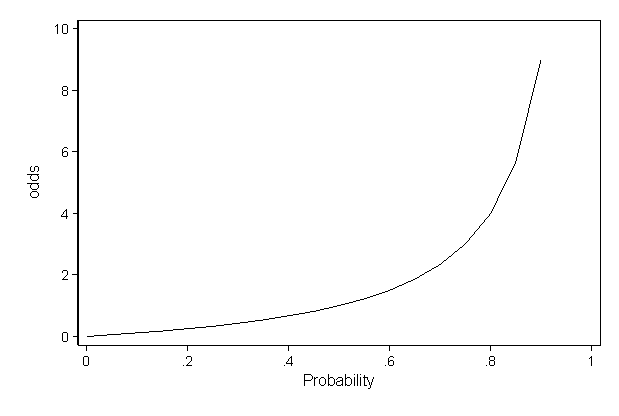
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsOdds and Odds Ratio If an event takes place with probability p, the odds in favor of the event are p 1 p to 1 p = 1 2 implies 1 to 1 odds;More on the Odds Ratio Ranges from 0 to infinity Tends to be skewed (ie not symmetric) "protective" odds ratios range from 0 to 1 "increased risk" odds ratios range from 1 to Example "Women are at 144 times the risk/chance of men" "Men are at 069 times the risk



How To Read Sports Odds Ratio
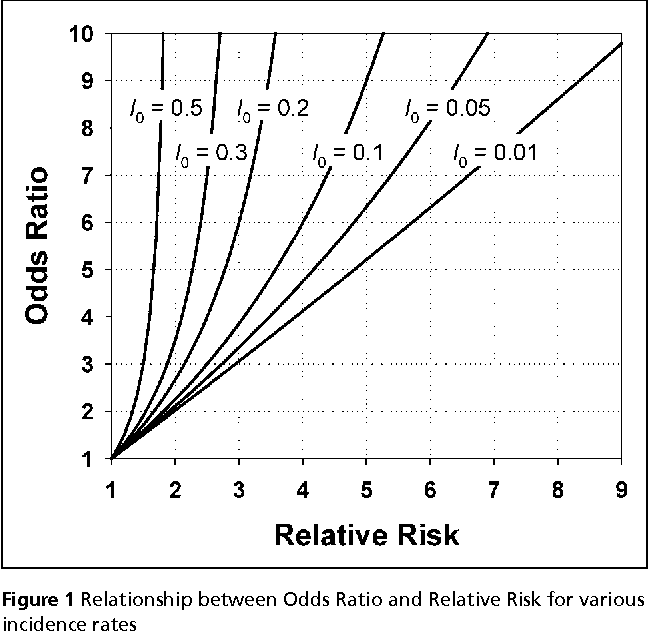


Table 1 From When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
Oct 31, 11 · Diagnostic odds ratios less than one indicate that the test can be improved by simply inverting the outcome of the test – the test is in the wrong direction, while a diagnostic odds ratio of exactly one means that the test is equally likely to predict a positive outcome whatever the true condition – the test gives no informationLet us now look at the relation between the relative risk and the odds ratio (Zhang and Yu, 1998) OR= ˇ 1 1 1ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 = ˇ ˇ 2 1 2 1 1 = RR 2 1 (21) From this we see that OR is always further away from 1 than RR But, more importantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998)Aug 26, · What's the Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios, Odds Ratios, and Hazard Ratios?



Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



A Piece Of My Mind Meta Analysis Effect Size Calculation
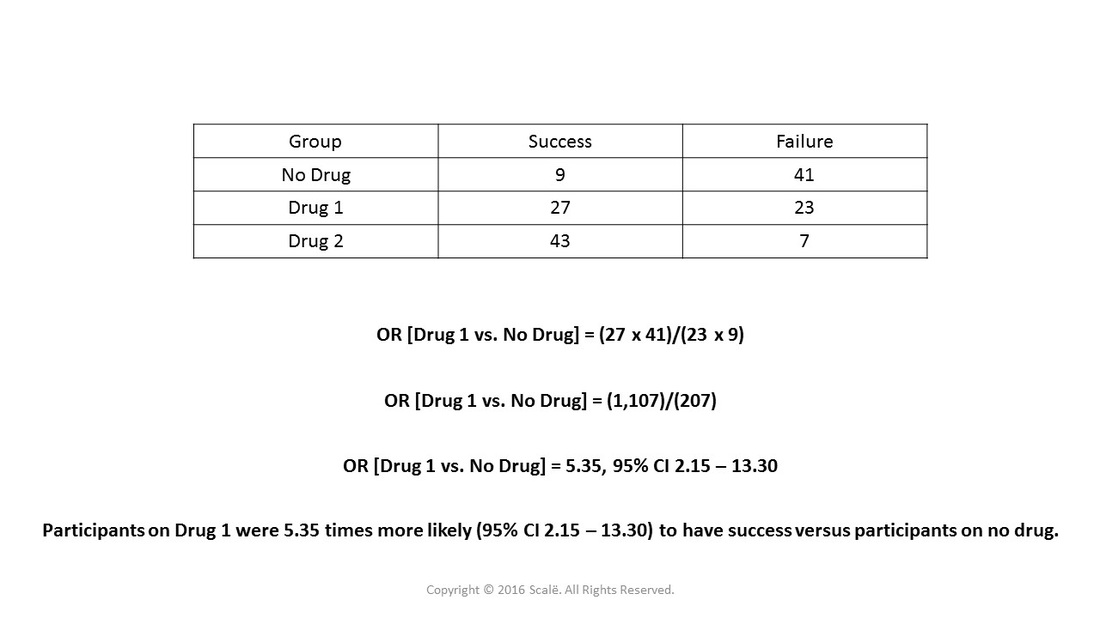
To calculate the odds ratio, we use one of the following formulas (both give the same outcome) Example 2 We compare smokers and nonsmokers with regard to the presence of ischemic heart disease The following table shows the results Example 2 We can now calculate the odds ratio (10/40) / (5/45) = 225Dec 08, 18 · Risk Ratio vs Odds Ratio Whereas RR can be interpreted in a straightforward way, OR can not A RR of 3 means the risk of an outcome is increased threefold A RR of 05 means the risk is cut in half But an OR of 3 doesn't mean the risk is threefold;Relative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / Probability



Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
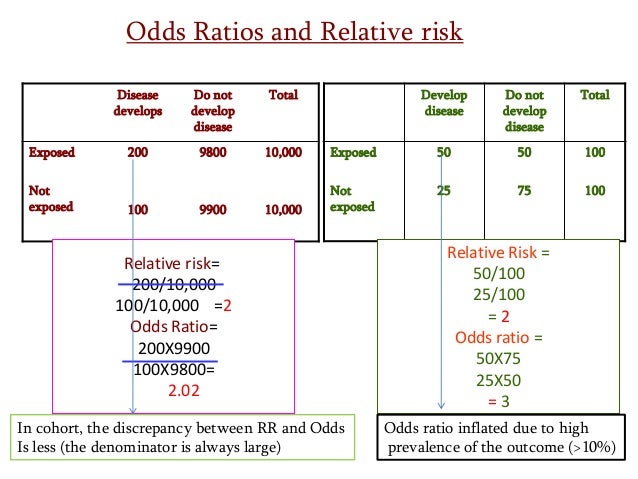


Estimating Risk



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey
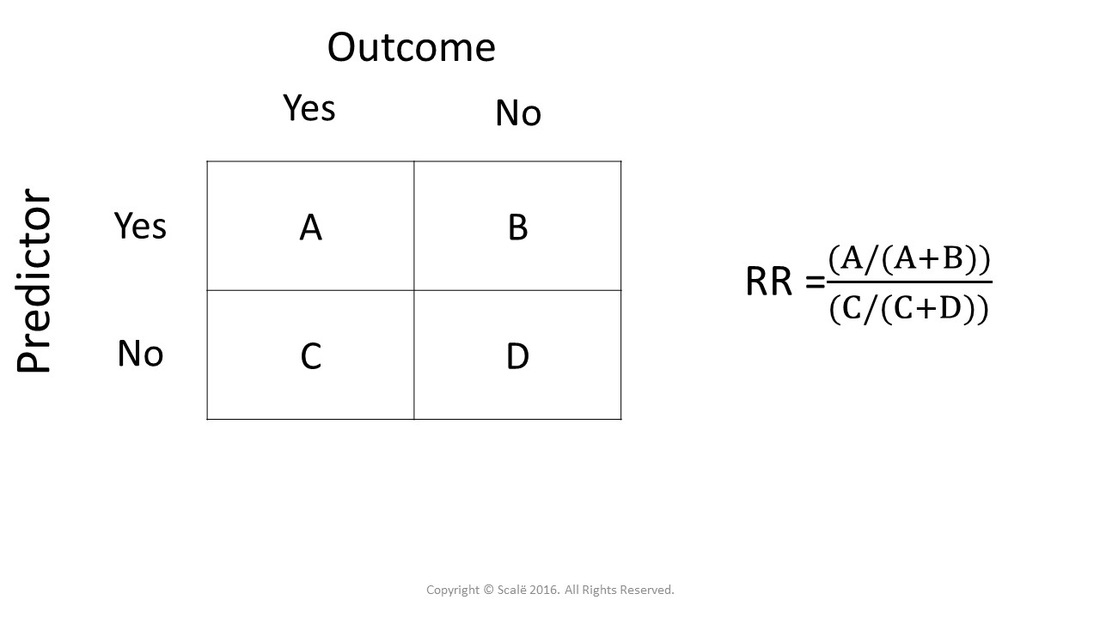


Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Epidemiology Odds Ratio Or Bean Around The World



Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Or2rr



What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1


27 Sep 01 Draft



Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh



Reporting The Results Sage Research Methods



Solved Week 4 Odds Ratio Calculation Interpretation Od Chegg Com



Solved Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Rati Chegg Com


Effect Modification Group C 1


Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Springerlink



Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube



Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated


27 Sep 01 Draft



Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine



How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube



Odds Ratio Wikipedia


Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things



Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
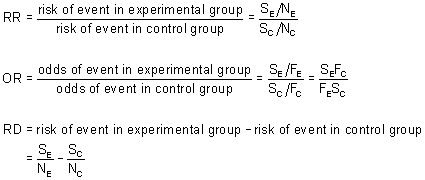


Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd


Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss



The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor


Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1


Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios


How To Interpret The Odd Ratio And P Value


Excel Odds Ratio Foodborne Disease Outbreak Toolkit



Relative Risk Http Www Slideshare Net Terryshaneyfelt7 What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean Study Skills Research Methods Study Tips


Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression



Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout
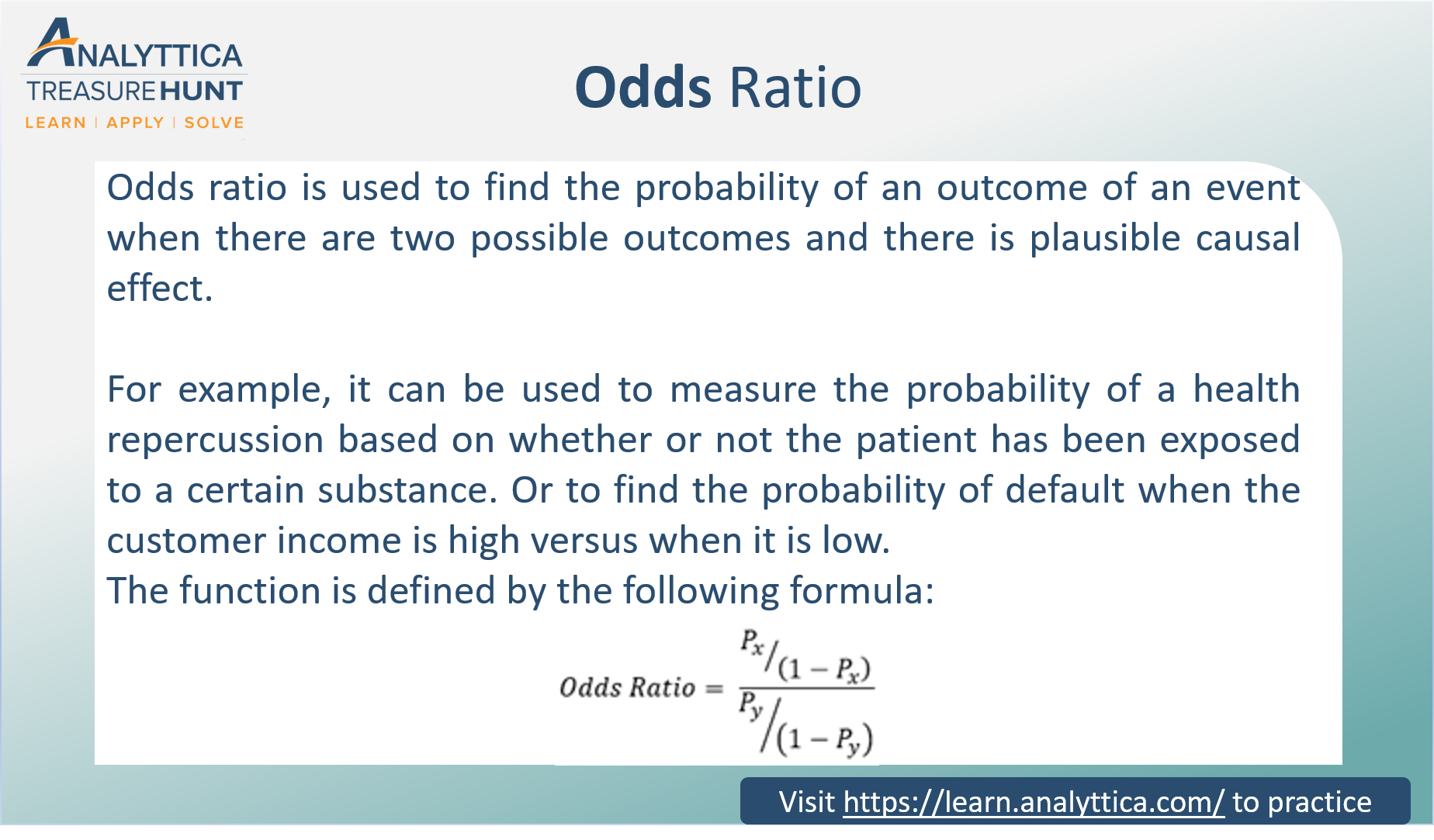


Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download



On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk


Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo



Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science



Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube



Image Result For Odds Ratio And Risk Ratio And Cohort Study And Case Study Cohort Study Case Study Study
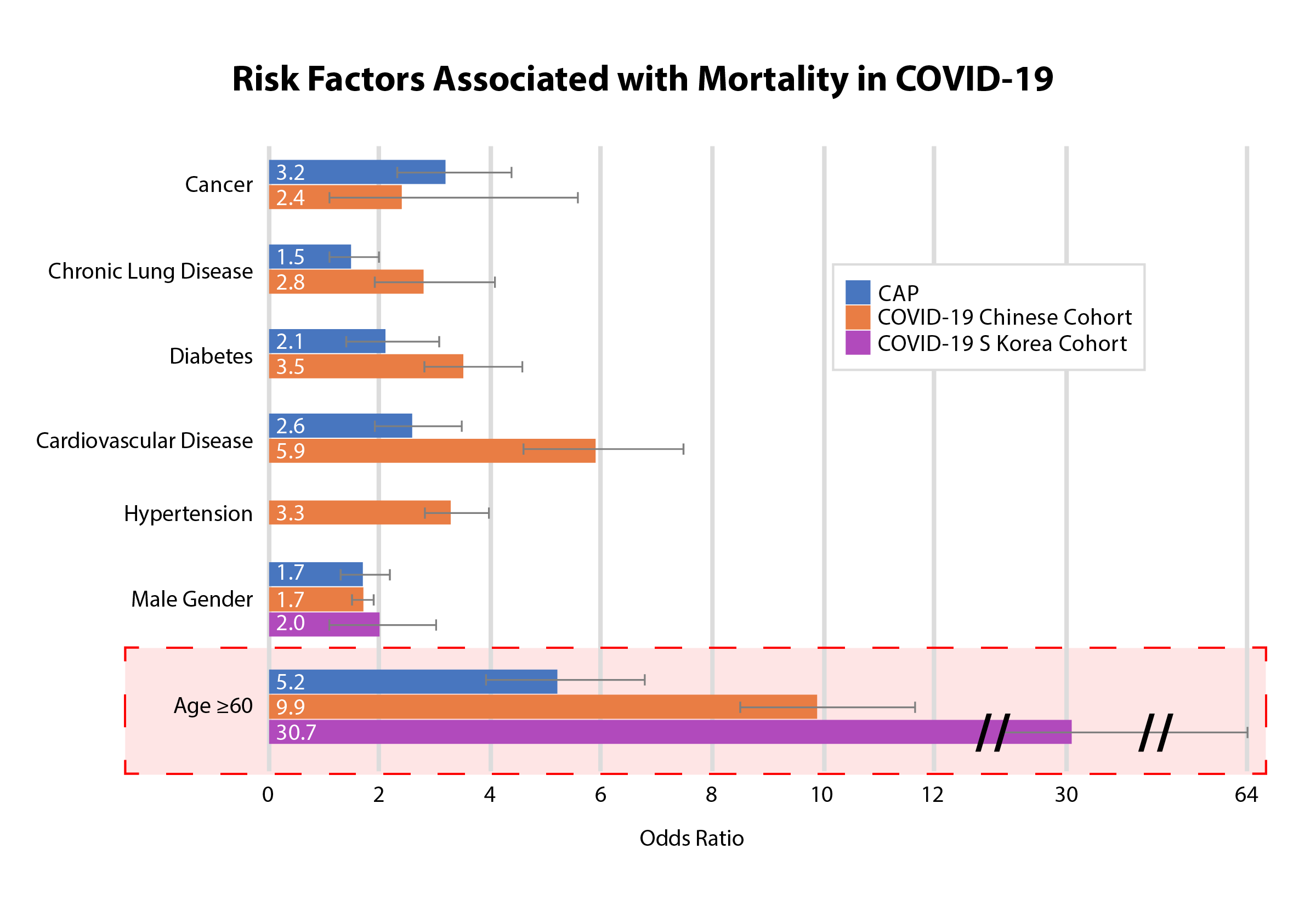


Nnt Review Odds Ratios Of Mortality Risk Factors



How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube



Odds Ratio Article



Calculation Of Ror Reporting Odds Ratio Contingency Table And Formula Download Scientific Diagram


Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data
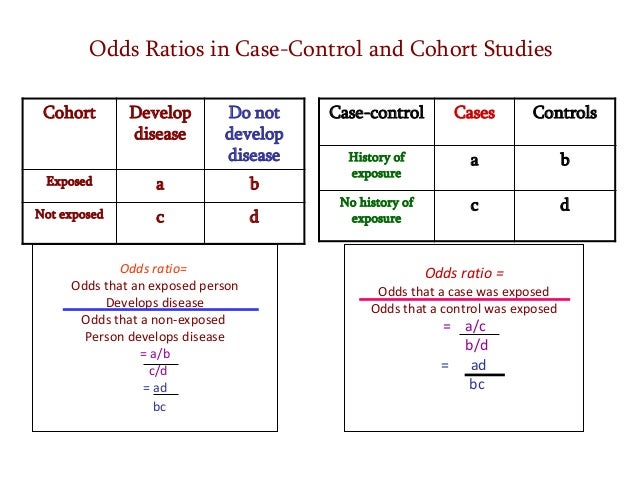


Estimating Risk
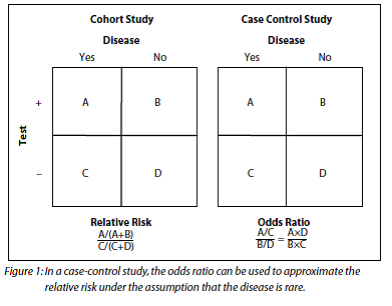


How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy
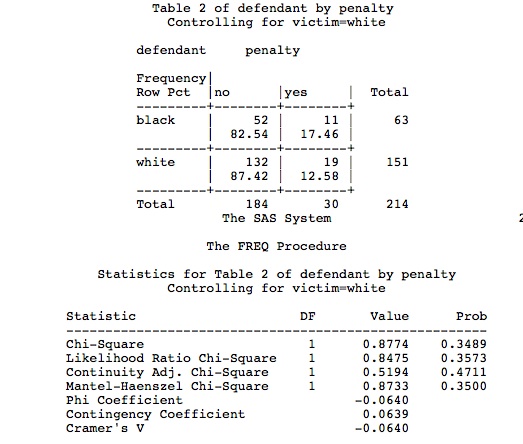


5 3 Marginal And Conditional Odds Ratios Stat 504



Conditional Probability Ppt Video Online Download


Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf


Relative Risk Odds Ratio
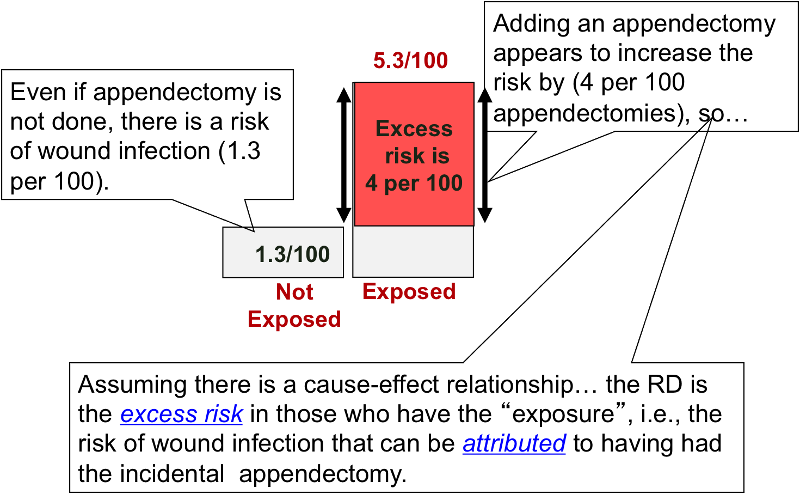


Risk Differences And Rate Differences
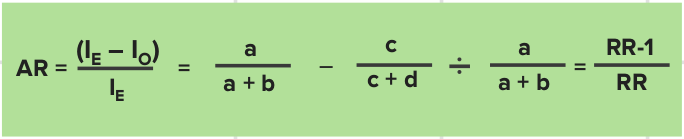


Attributable Risk And Odds Ratio Online Medical Library



Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk



Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube



A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Relative Risk Wikipedia



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿