(A medically induced coma, by contrast, ends when the drugs that are inducing the coma are cut off, thus arousing the patient) Comas are by definition states from which you can't be arousedT he neurologist is often required to evaluate the unconscious patient from both the diagnostic and prognostic perspective Knowledge of the anatomical basis of coma is essential for competent evaluation but must be combined with an understanding of the many, often multifactorial, medical conditions that result in impaired consciousness Consciousness is a state of awareness of self and theA fully conscious patient has a Glasgow Coma Score of 15 A person in a deep coma has a Glasgow Coma Score of 3 (there is no lower score) The Rancho Level of Cognitive Functioning Scale (LCFS) is a scale used to assess cognitive functioning in people with brain injury 11 The first three levels are similar to the stages of coma, VS, and MCS This scale is most often used in the first year

Position Statement Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Of Patients With Confirmed Or Suspected Covid 19
Semi comatose patient position
Semi comatose patient position-S xyz The three values of Image Position (Patient) (00,0032) It is the location in mm from the origin of the RCS X xyz The values from the row (X) direction cosine of Image Orientation (Patient) (00,0037) Y xyz The values from the column (Y) direction cosine of Image Orientation (Patient) (00,0037) i Column index to the image planeAssisting Patient to the Sitting Position Patients who have been immobile for a long period of time may experience vertigo, a sensation of dizziness, and orthostatic hypotension, a form of low blood pressure that occurs when changing position from lying down to sitting, making the patient feel dizzy, faint, or lightheaded (Potter, Perry, RossKerr, & Wood, 10)



Prone Position As Prevention Of Lung Injury In Comatose Patients A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study Semantic Scholar
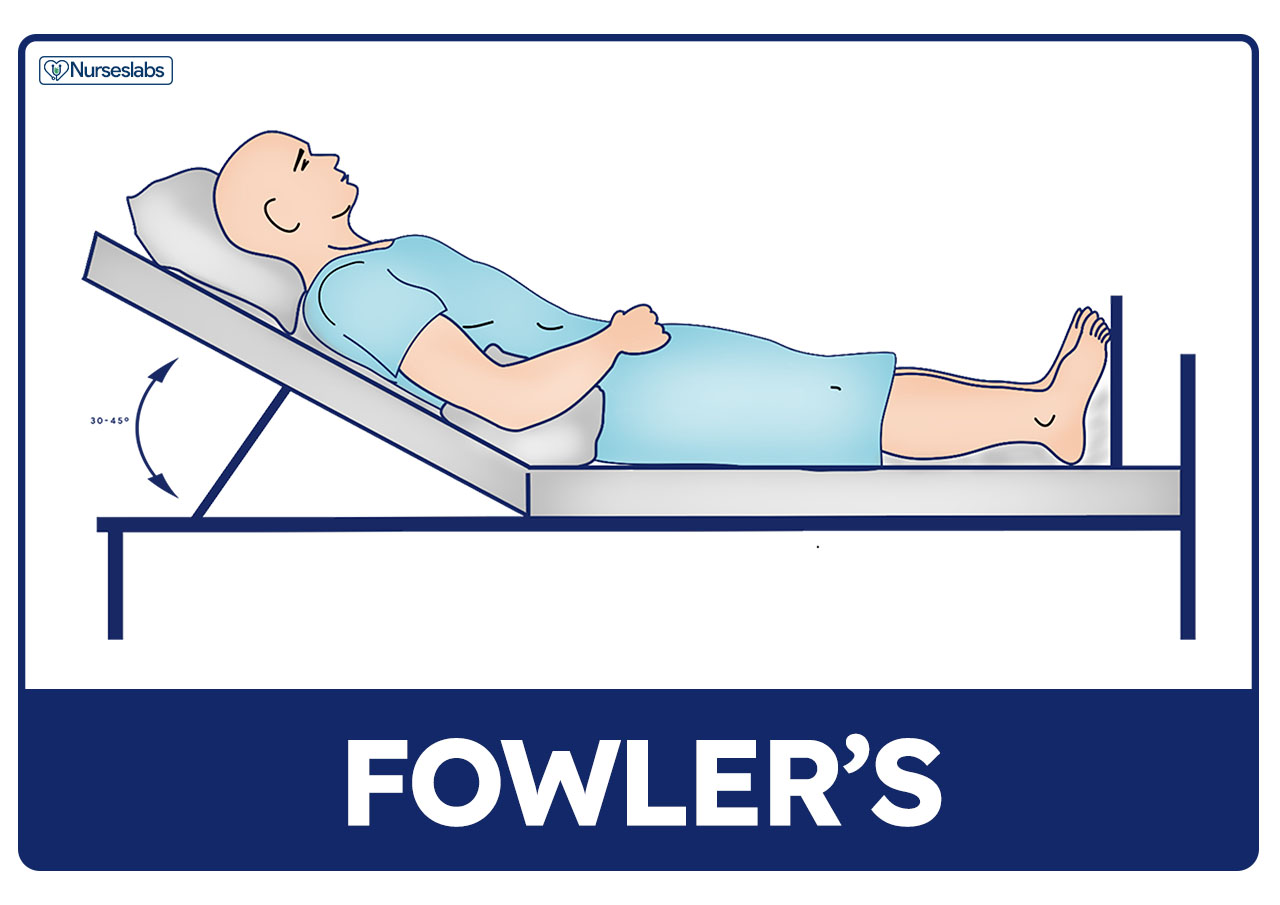
A fully conscious patient has a Glasgow Coma Score of 15 A person in a deep coma has a Glasgow Coma Score of 3 (there is no lower score) The Rancho Level of Cognitive Functioning Scale (LCFS) is a scale used to assess cognitive functioning in people with brain injury 11 The first three levels are similar to the stages of coma, VS, and MCS This scale is most often used in the first yearVary position of the bed, turn and reposition patient, and chest physical therapy What is the cause of altered nutrition in the patient who is in a coma?Fowler's position is known as the "standard patient's position," and was invented by George Ryerson Fowler Certified registered nurses are trained in their RN programs to recognize this type of patient position because it provides the most comfort The technique is used for a variety of reasons, including
T he neurologist is often required to evaluate the unconscious patient from both the diagnostic and prognostic perspective Knowledge of the anatomical basis of coma is essential for competent evaluation but must be combined with an understanding of the many, often multifactorial, medical conditions that result in impaired consciousness Consciousness is a state of awareness of self and theComa is a presenting symptom in approximately 051% of emergency department admissions, although the only paper addressing frequency of coma in the ED dates from 1934, citing coma as the presentation in 3% of admissions to the ED A more recent retrospective analysis found alteration of mental status in between 4% and 10% of ED patients Disturbances may be caused by a wide variety ofIn fact, the diagnoses of the patients in
A patient who is comatose, experiences spasticity, has extensive paralysis, or is unable to mentally or physically maintain a safe position may require some form of temporary restraint or protective positioning These protective measures are to be differentiated from the use of restraints for a prolonged periodComa is unresponsiveness from which the patient cannot be aroused and in which the patient's eyes remain closedImpaired consciousness refers to similar, less severe disturbances of consciousness;Well that depends on the nature of injury or illness that resulted in the person being in a coma If there is a hemiplegia (paralysis of one side) the position is to normalise muscle tone and maintain range of movement If there are fractures, the positioning becomes complicated but still important
/GettyImages-659064405-4e9c1e86abad45c38655543702a8d989.jpg)


What To Know When Deciding About Feeding Tubes



Neurological Assessment Of Coma Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
Fowler's Position Fowler's position, also known as sitting position, is typically used for neurosurgery and shoulder surgeries The beach chair position is often used for nasal surgeries, abdominoplasty, and breast reduction surgeries When positioning a patient in Fowler's position, the surgical staff should minimize the degree of the patient's head elevation as much as possible and alwaysHowever, the authors noted that important limitations of this study included small sample size, they could not control family members talking to the patient, and they did not work with a group of patients with the same diagnosis;Prone Positioning for Nonintubated Patients Although prone positioning has been shown to improve oxygenation and outcomes in patients with moderatetosevere ARDS who are receiving mechanical ventilation, 7,8 there is less evidence regarding the benefit of prone positioning in awake patients who require supplemental oxygen without mechanical



Neuroanesthesia Section 4 Gupta And Gelb S Essentials Of Neuroanesthesia And Neurointensive Care


3 5 Positioning Patients In Bed Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient Care
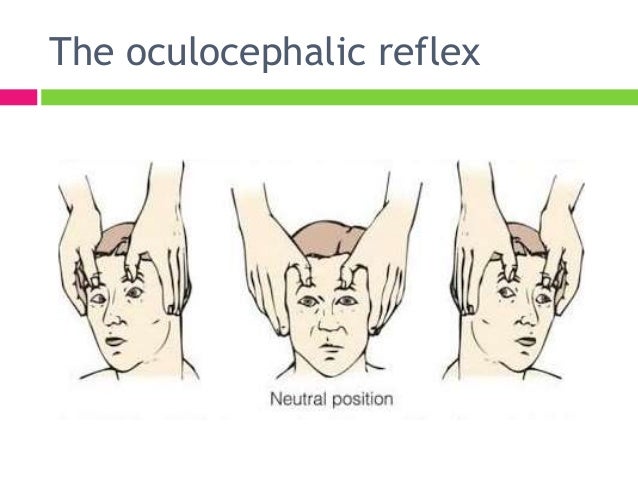
Caregivers of a person who is in coma or recently recovering from a coma, they may have many concerns and questions in trying to cope with a serious illness This guide was developed as a result of the need we identified, when our 29yearold daughter, Jill Elizabeth Russell Eddy was in coma for 12 monthsThe eyes should gradually return to the midposition in a smooth, conjugate movement if the brainstem is intact Patients with metabolic coma (eg hepatic failure) may have exaggerated, brisk oculocephalic reflexes Oculovestibular reflex (caloric stimulation)These disturbances are not considered coma The mechanism for coma or impaired consciousness involves dysfunction of both cerebral hemispheres or of the reticular activating system (also known as the
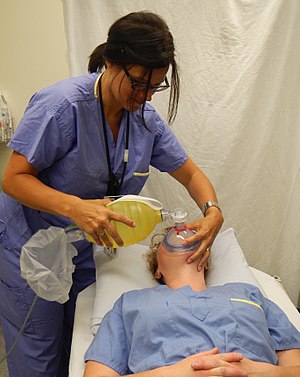


Respiratory Arrest Wikipedia


3 5 Positioning Patients In Bed Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient Care
Several observations in 'comatose' patients followed the experimental findings described below Observations on the pupils were noted by Cheyne , (ii) increasing the filling of the heart by positioning the patient or compression of the abdomen, or by infusion of salt solution and (iii) by drugs, including atropine, strychnine,Swing the patient's feet off the edge of the bed and move them into a sitting position Place 1 arm under the patient's shoulders and 1 arm behind their knees Bend your knees as you swing the patient's feet off the edge of the bed Shift your weight to your back foot and gently ease them into an upright sitting position, facing youThe following steps should be followed to make sure the patient is in the right position Make sure the patient's ankles, knees, and elbows are not resting on top of each other Make sure the head and neck are in line with the spine, not stretched forward, back, or to the side Return the bed to a comfortable position with the side rails up


Approach To The Comatose Patient



Pdf Is The Supine Position Associated With Loss Of Airway Patency In Unconscious Trauma Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis
If a patient is comatose, it is safe to assume that the nervous system is being affected at the brainstem level or above The goal of a neurological examination in a comatose patient is to determine if the coma is induced by a structural lesion or from a metabolic derangement, or possibly from bothKraske/Jacknife position The patient begins in the supine position again, and is logrolled after anesthesia to the prone position The OR table is then flexed to a 90degree angle;The eyes should gradually return to the midposition in a smooth, conjugate movement if the brainstem is intact Patients with metabolic coma (eg hepatic failure) may have exaggerated, brisk oculocephalic reflexes Oculovestibular reflex (caloric stimulation)



1 428 Coma Patient Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images


Recovery Position Wikipedia
Following are guidelines for improving the arousal of the comatose patients Approaching the Patient • Make the patient identify you • Talk to the patient slowly and in a normal tone of voice • Keep sentences short and give the patient extra time to think about what you have said and repeat it a few timesOr others prefer to study in groups This 15item NCLEXRN practice questions will give you familiarization about patient positioning "You measure the size of the accomplishment by the obstacles you had to overcome to reach your goalsProne Positioning for Nonintubated Patients Although prone positioning has been shown to improve oxygenation and outcomes in patients with moderatetosevere ARDS who are receiving mechanical ventilation, 7,8 there is less evidence regarding the benefit of prone positioning in awake patients who require supplemental oxygen without mechanical



Recommended Treatment Algorithm For Patients With Traumatic Posterior Download Scientific Diagram
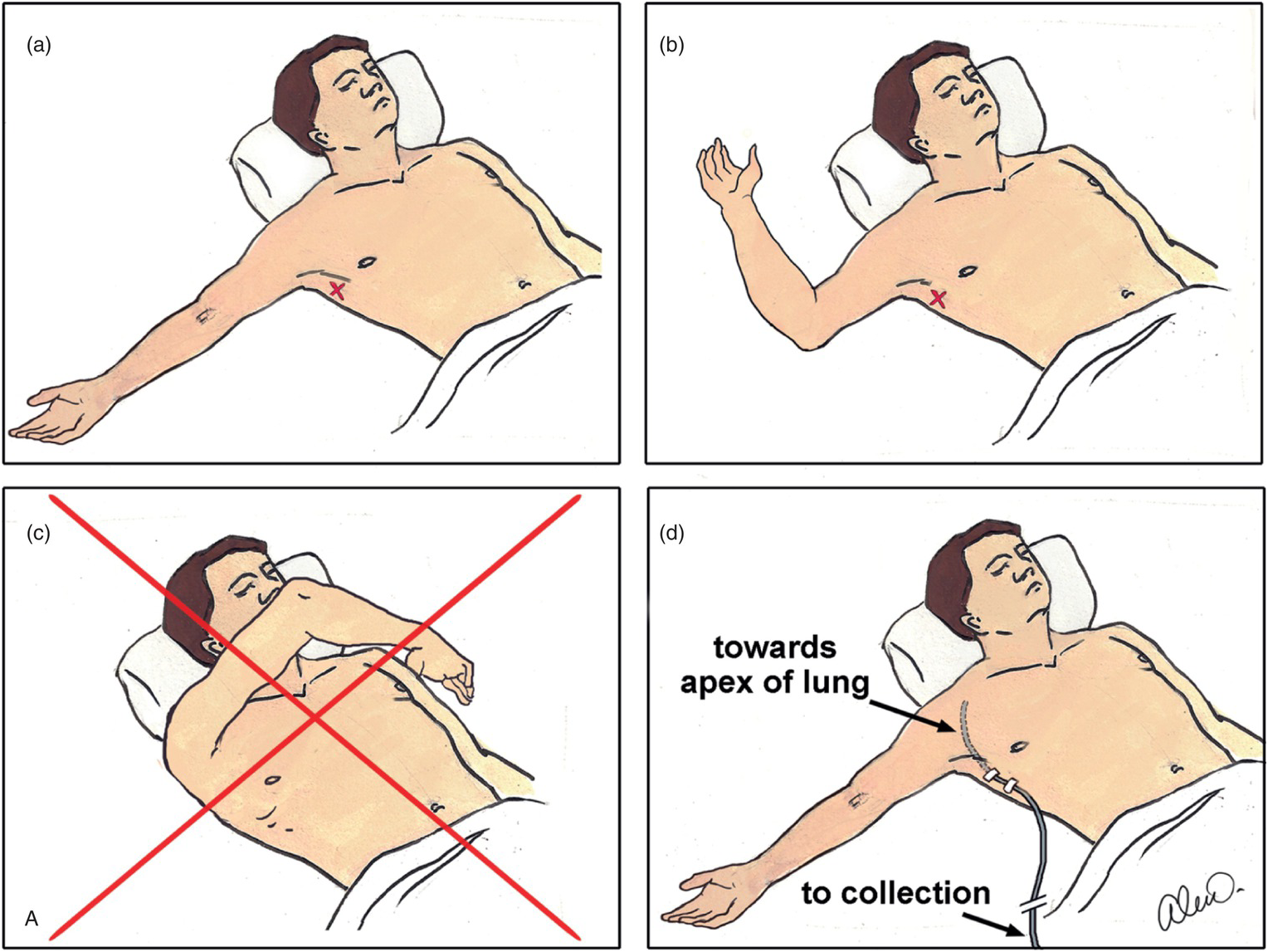


Pulmonary Trauma Chapter 13 The Emergency Medicine Trauma Handbook
Standard Lithotomy Position The patient's hips are flexed until the angle between the posterior surface of the patient's thighs and the OR bed surface is 80 degrees to 100 degrees The patient's lower legs are parallel with the OR bed Hemilithotomy Position The patient's nonoperative leg is positioned in standard lithotomy The patient's operative leg may be placed in tractionWhat is the correct position?A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wakesleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions Coma patients exhibit a complete absence of wakefulness and are unable to consciously feel, speak or move Comas can be derived by natural causes, or can be medically


My 17 Days In A Coma Fighting Pneumonia And Sepsis In Icu Belfast News Letter



Chest Radiology
Auditory stimulation is associated with higher GCS in comatose patients;Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) The GCS is used across the world and is a means of scoring a patient's conscious level It is also useful to monitor progress of the patient The GCS is determined by assessing three aspects eye opening (four levels), verbal response (five levels) and motor response (six levels)An insulted nervous system causes this
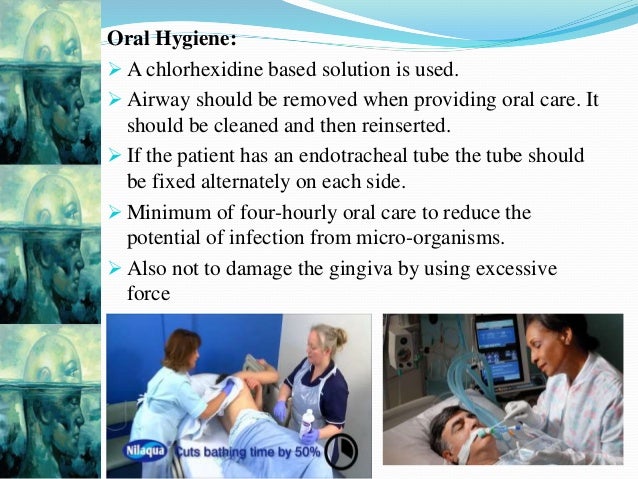


Care Of An Unconcious Patient


3 5 Positioning Patients In Bed Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient Care
The patient has no gag reflex The movement of the breathing tube (in and out) or the insertion of a smaller tube down the breathing tube will cause a gag reflex in a comatose patient, but will not elicit a reflex in the braindead patient The patient has no spontaneous respirationConclusion Whether you're reading a new physician order to place the patient in HighFowler's position, documenting the position the patient was in, or suggesting a patient position to the MD, after utilizing this resource, you'll feel more comfortable and confident While this is a basic aspect of nursing care, it can be confusing and difficult to remember, especially in a chaotic momentIn fact, the diagnoses of the patients in


How Does Being In A Coma Affect A Person In The Long Term Multiple Years Quora
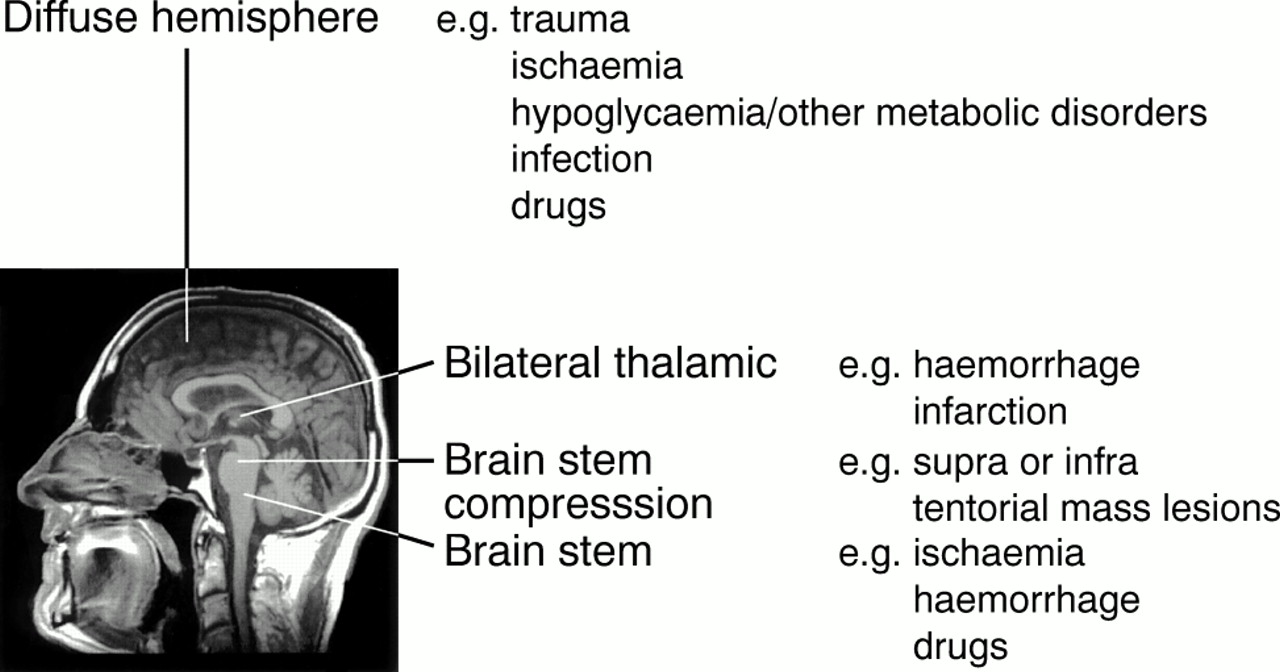


Neurological Assessment Of Coma Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
Body positions that minimize aspiration include the reclining position, chin down, head rotation, side inclination, the recumbent position, and combinations of these Patients with severe dysphagia often use a 30° reclining position But in reality, the patient must be more than 60° higher than a supine position in order to eat withoutEg E4V5M6 = GCS 15) the pattern ofFind a study method that works best For some, it means locking themselves in a room, studying alone in coffee shops;
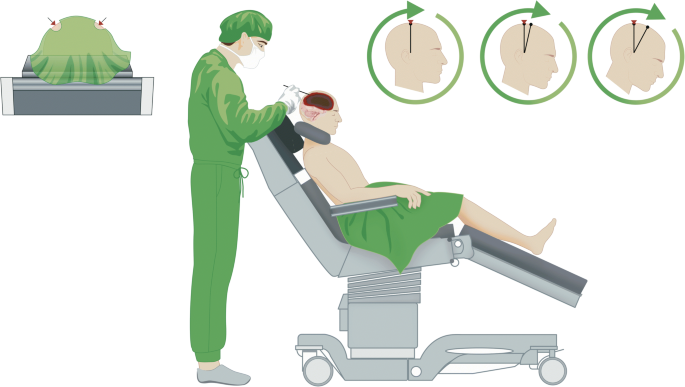


Awake Surgery In Sitting Position For Chronic Subdural Hematoma Springerlink
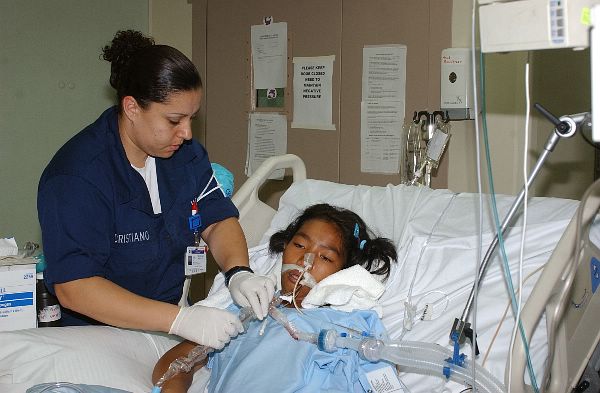


Recovery Room Care Of The Surgical Patient Multimedia Edition
Supine position Prone position Patient lies on stomach with head turned to the side Prone position Lateral position Patient lies on the side of the body with the top leg over the bottom leg This position helps relieve pressure on the coccyx Lateral position Sims position Patient lies between supine and prone with legs flexed in front of the patientLawyers for the comatose woman who was raped and later gave birth at Hacienda Healthcare in Phoenix, Arizona have said she was raped repeatedly and may have been impregnated beforeThe study shows that, within the frame of abnormal motor responses, the same patient can exhibit different reactions according to the site of stimulation and initial position of the upper extremities These patterns are fairly constant and should be borne in mind in the evaluation of comatose patients



Pdf Prone Position As Prevention Of Lung Injury In Comatose Patients A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study



05 Oral Care Unconscious Resident Youtube
(A medically induced coma, by contrast, ends when the drugs that are inducing the coma are cut off, thus arousing the patient) Comas are by definition states from which you can't be arousedA patient who awakens from a coma may also develop a socalled lockedin syndrome, being completely conscious but paralyzed and unable to communicate, except through eye blinksThe patient's arms are at the sides or on arm boards This position is used almost exclusively for rectal surgery The equipment used is the same for the prone


Repositioning Patients To Prevent Pressure Injuries Shield Healthcare


Approach To The Comatose Patient
Position the patient, position the airway and maintain the proper airway position Lay the patient supine If a stretcher is available, position the patient on it quickly, with the patient ideallyReviewed and revised 30 March 15 OVERVIEW Coma Coma is a state of unconsciousness caused by temporary or permanent impairment of the ascending reticular system in the brainstem, or both cerebral hemispheres The key components of the neurological examination of the comatose patient are level of consciousness (Glasgow Coma Score — list the components;Mental status is evaluated by observing the patient's response to visual, auditory and noxious (ie, painful) stimuli The three main maneuvers to produce a noxious stimulus in a comatose patient are 1 press very hard with your thumb under the bony superior roof of the orbital cavity, 2 squeeze the patient's nipple very hard, and 3 press a



How To Perform Oral Care For Unconscious Patient In Hospital
/Recovery-56a2f6293df78cf7727b4d8e.jpg)


Recovery Position In First Aid Treatment
Auditory stimulation is associated with higher GCS in comatose patients;Check the 6 operating tables surgical positions and watch 5 videos on patient positioning examples Pick the one that fits your discipline Optimal positioning not only ensures the best possible access to the surgical site, but also prevents longterm consequences such as nerve damage or pressure ulcers These secondary complications can delay rehabilitation and recoveryThe presence of the tube keeps the gastroesophageal sphincter, between the esophagus and stomach, open Combine this with the reclining position of comatose patients, the fact that normal



1 428 Coma Patient Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images



Is The Supine Position Associated With Loss Of Airway Patency In Unconscious Trauma Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Scandinavian Journal Of Trauma Resuscitation And Emergency Medicine Full Text
However, the authors noted that important limitations of this study included small sample size, they could not control family members talking to the patient, and they did not work with a group of patients with the same diagnosis;Positions included the "Coma Position", "Rautek's Position" and the "HAINES (High Arm IN Endangered Spine) position" In 1992, the European Resuscitation Council adopted a new position where the arm nearest the floor was brought out in front of the patient, whereas it had previously been placed behind the patientPosition Statements All post cardiac arrest comatose patients, regardless of their initial rhythm (shockable vs nonshockable) and location of arrest (outofhospital or inhospital cardiac arrest OHCA/IHCA) should be evaluated for active TTM Active cooling should be considered and begin as soon as possible, and for up to 12 hours after ROSC



Nursing The Unconscious Patient



Top 10 Essentials Care Of Patients On Ventilators American Nurse
Once patient is on her side, pull both knees forward a bit, with the top knee higher than the bottom Put a pillow between the knees, calves and under the top foot, to keep the pressure off theHowever, comatose patients do not open their eyes, nor do they speak Their condition may resolve in a few days or weeks, or the patient may progress to a vegetative state, according to Johns


Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide
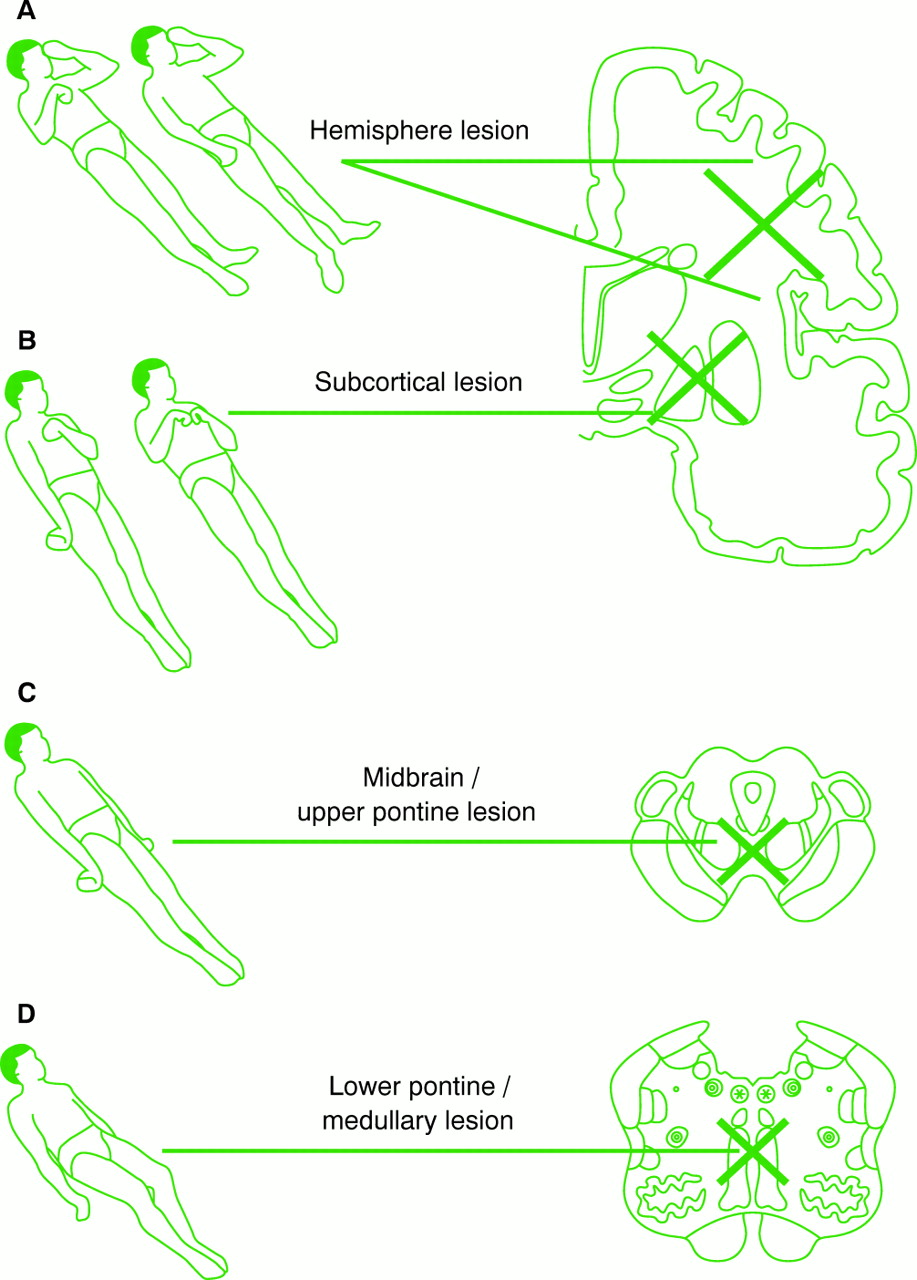


Neurological Assessment Of Coma Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry


Permanent Coma Patient Re Learned To Speak Via Coordination Dynamics Therapy



Patient Positioning Pictures Cheat Sheet For Nursing Students
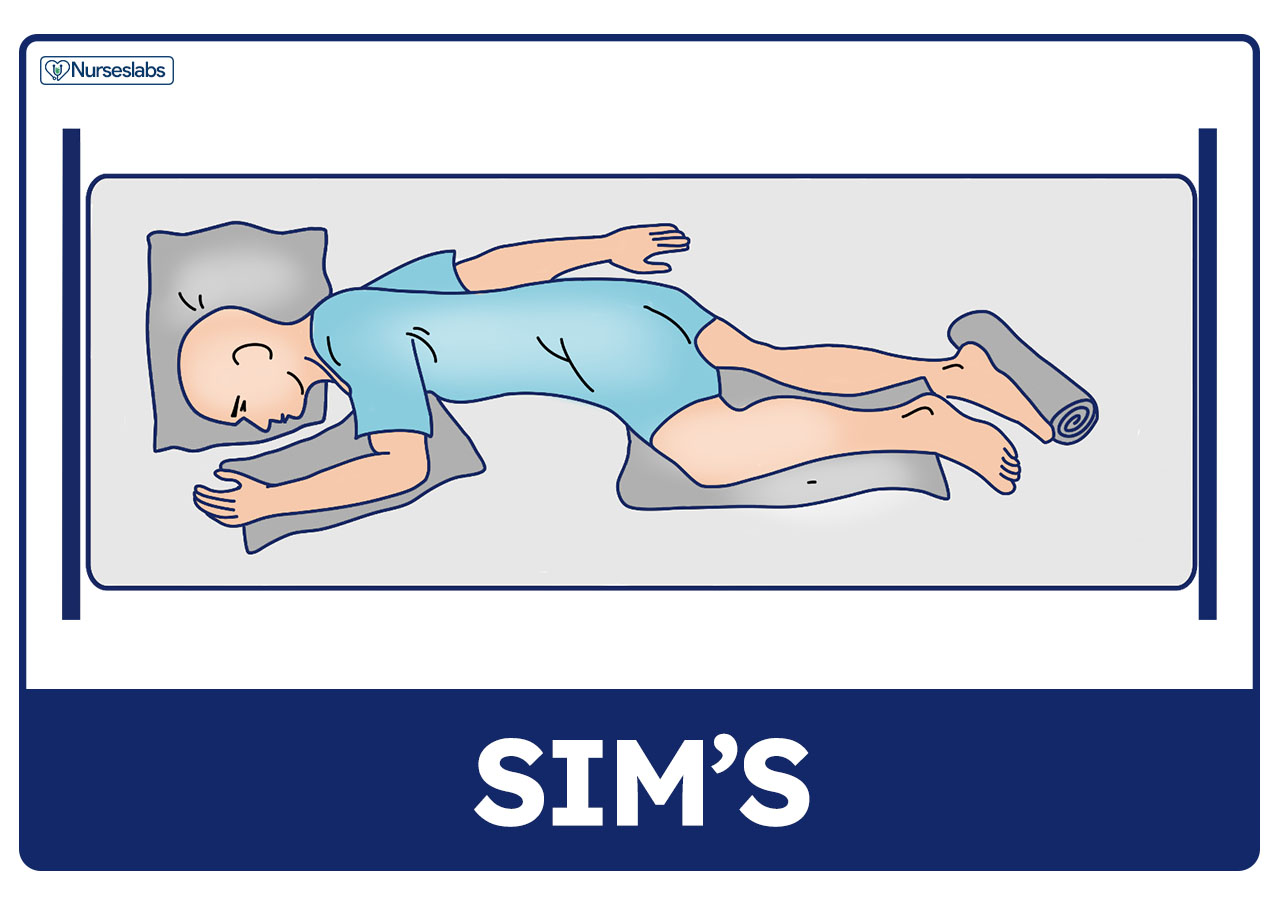


Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide


Tracheal Intubation Wikipedia
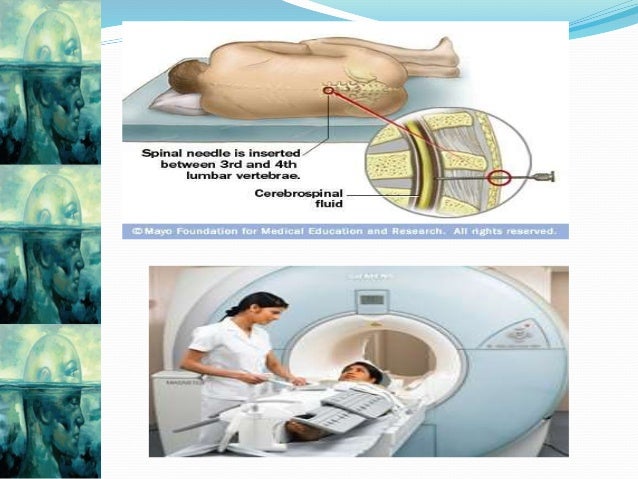


Care Of An Unconcious Patient


How To Ensure Patient Observations Lead To Effective Management Of Altered Consciousness Nursing Times


Teen Explains What Life Is Like In A Coma Abc News



Care Of An Unconcious Patient



Vegetative State Diagnosis Symptoms Treatment More


How To Perform A Lumbar Puncture



How To Do Orotracheal Intubation Using Video Laryngoscopy Critical Care Medicine Msd Manual Professional Edition



Teen Explains What Life Is Like In A Coma Abc News



Mosby S Nursing Video Skills


Care Of An Unconcious Patient



Acute Brain Dysfunction Prolonged In Covid 19 Icu Patients Medpage Today



Prone Position As Prevention Of Lung Injury In Comatose Patients A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study Semantic Scholar



Bathing Brushing The Teeth Combing The Hair Dressing Shaving Applying Makeup Patients Should Be Encouraged To Do As Much For Themselves As Possible Ppt Download


Coma Exam



Overview Of Coma And Impaired Consciousness Neurologic Disorders Msd Manual Professional Edition
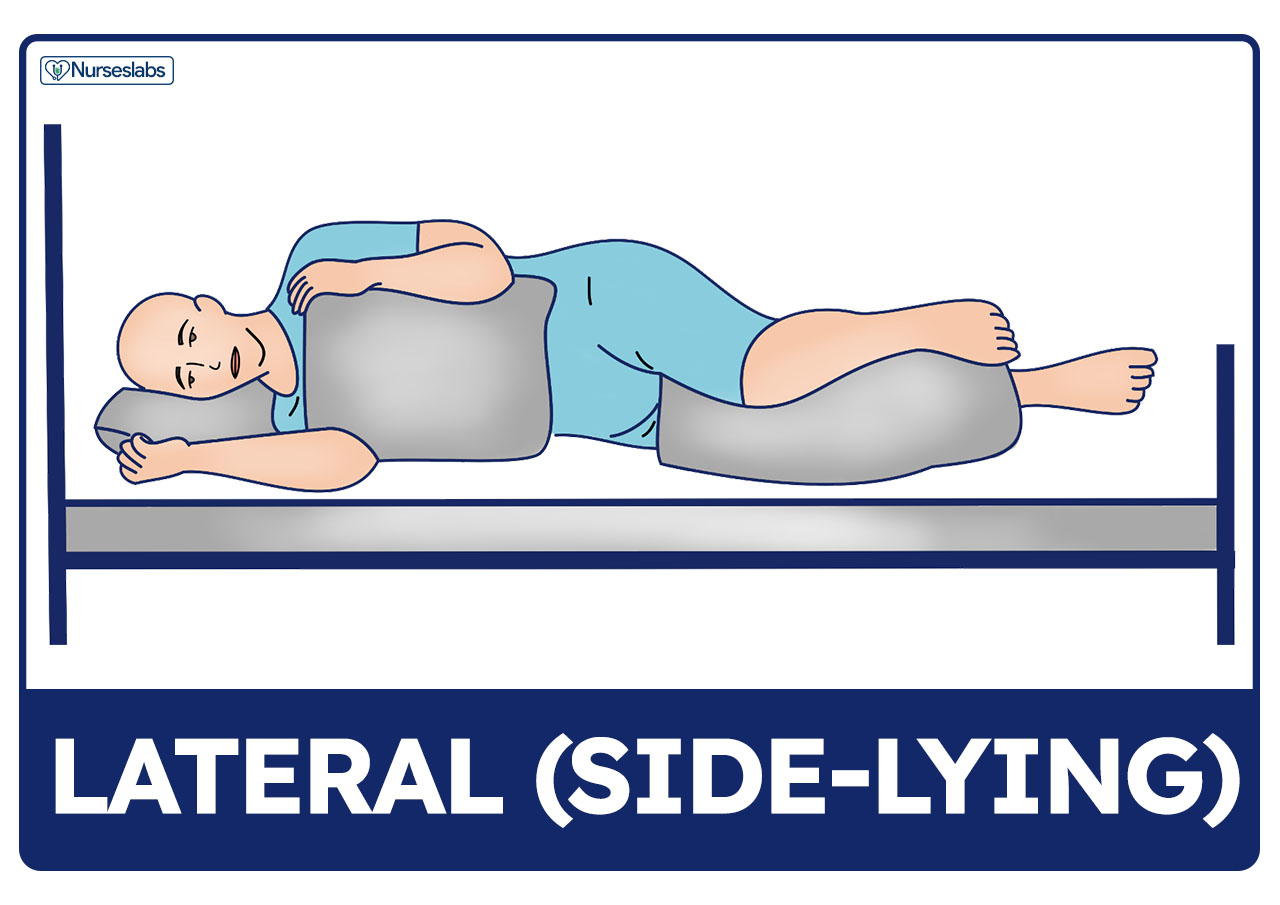


Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide



1 428 Coma Patient Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images



Cardiac Arrest In Pregnancy Circulation



Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide



First Aid For Unconsciousness Symptoms Treatment Causes More


New Research May Help Unlock Vegetative And Minimally Conscious Patients


Coma Position Stock Photo Alamy



How Uroshield Can Help Patients Who Are Unconscious Uroshield



Bedside External Ventricular Drain Placement For Haemorrhagic Stroke Patients With Brain Herniation And Acute Hydrocephalus A Case Series Woo 18 Surgical Practice Wiley Online Library



Why Are Patients In Permanent Comas Routinely Kept Alive



Position Statement Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Of Patients With Confirmed Or Suspected Covid 19
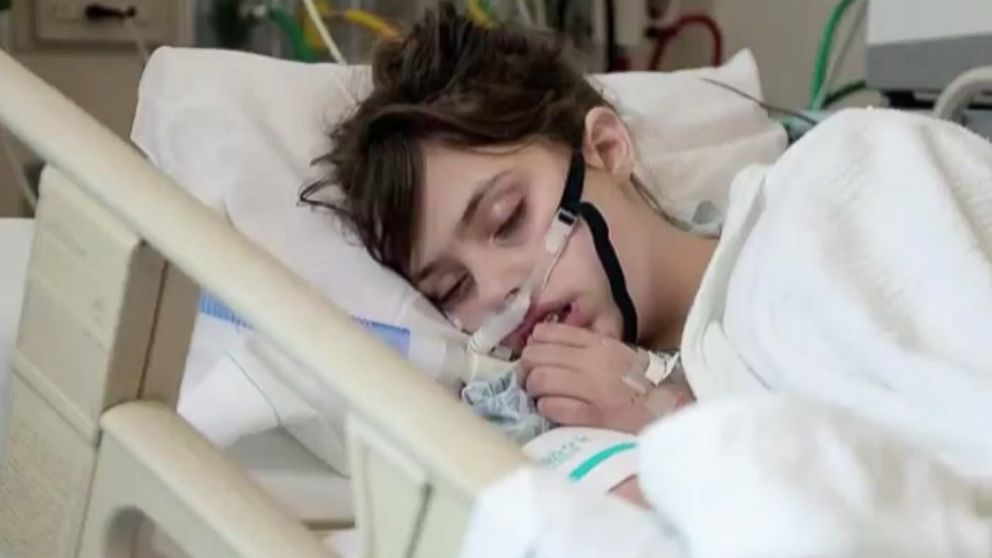


Teen Explains What Life Is Like In A Coma Abc News
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1221059141-0eb766d41a574563b9907cad9e3995ab.jpg)


Recovery Position In First Aid Treatment
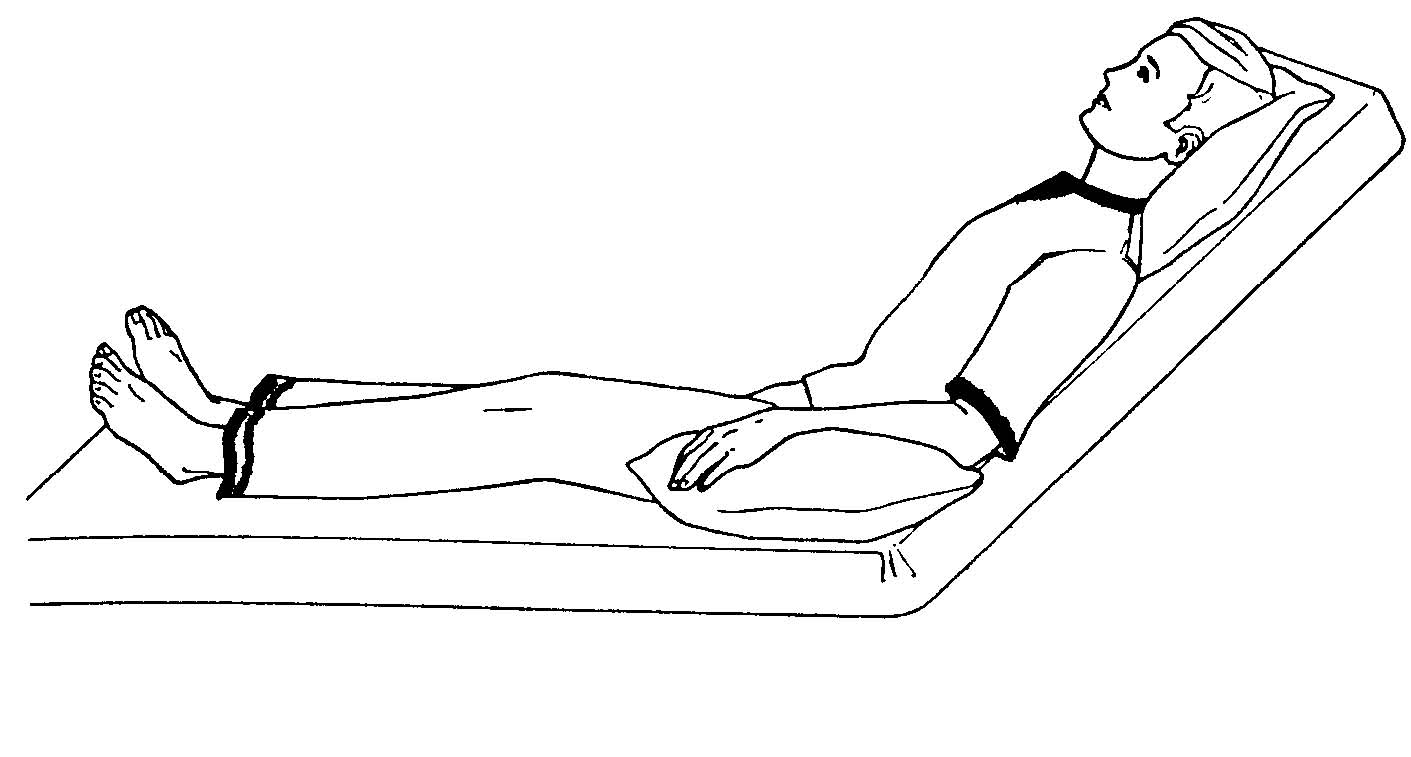


Recovery Room Care Of The Surgical Patient Multimedia Edition



Coronavirus How Physiotherapists Are Helping Patients Recover
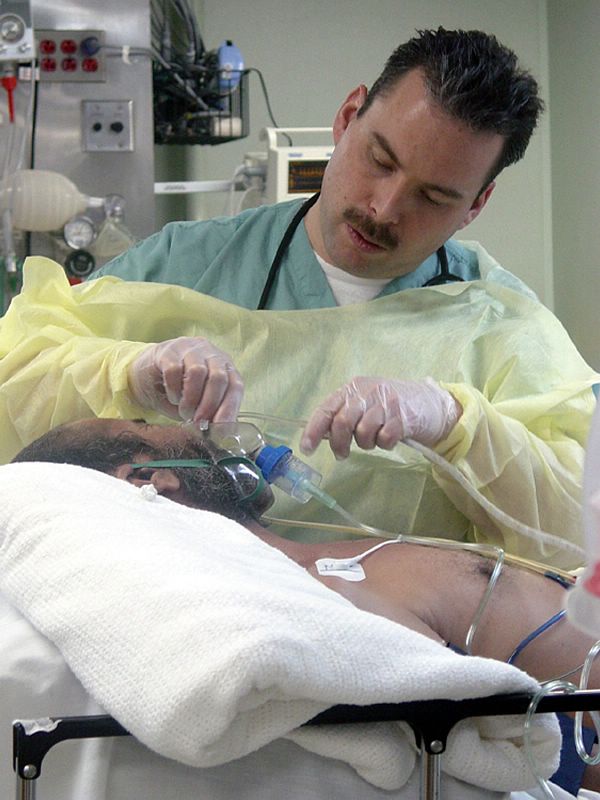


Recovery Room Care Of The Surgical Patient Multimedia Edition



Coma Usmf
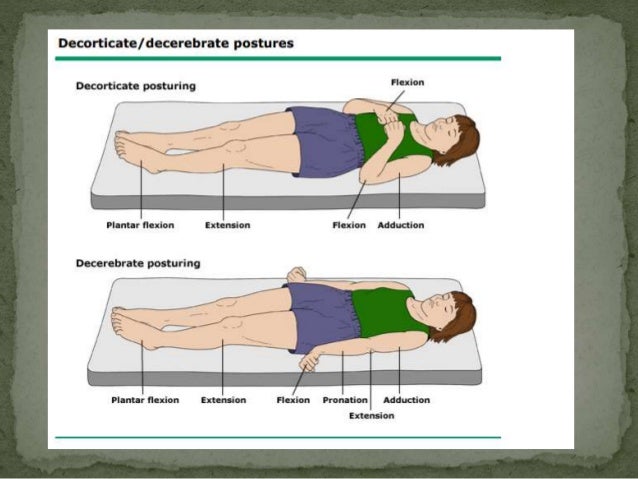


Approach To The Comatose Patient



Neurological Assessment 1 Assessing Level Of Consciousness Nursing Times
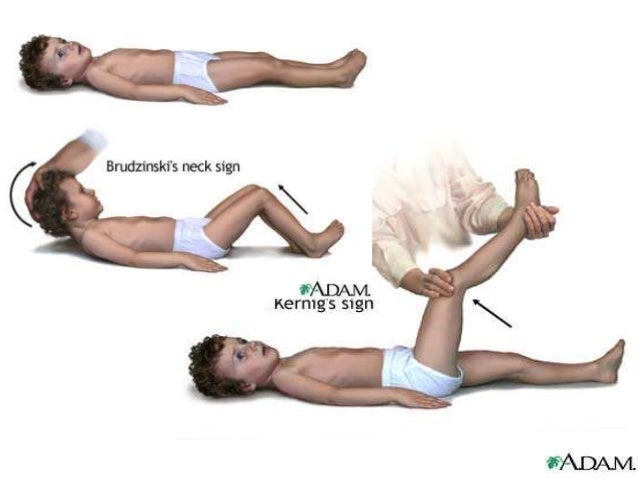


Approach To The Comatose Patient



Approach To The Comatose Patient


How To Perform A Lumbar Puncture



Patient Positioning 1 Supine Position Youtube



Unconscious Oral Care Youtube



Position Statement Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Of Patients With Confirmed Or Suspected Covid 19



How To Turn And Reposition An Immobile Patient Youtube
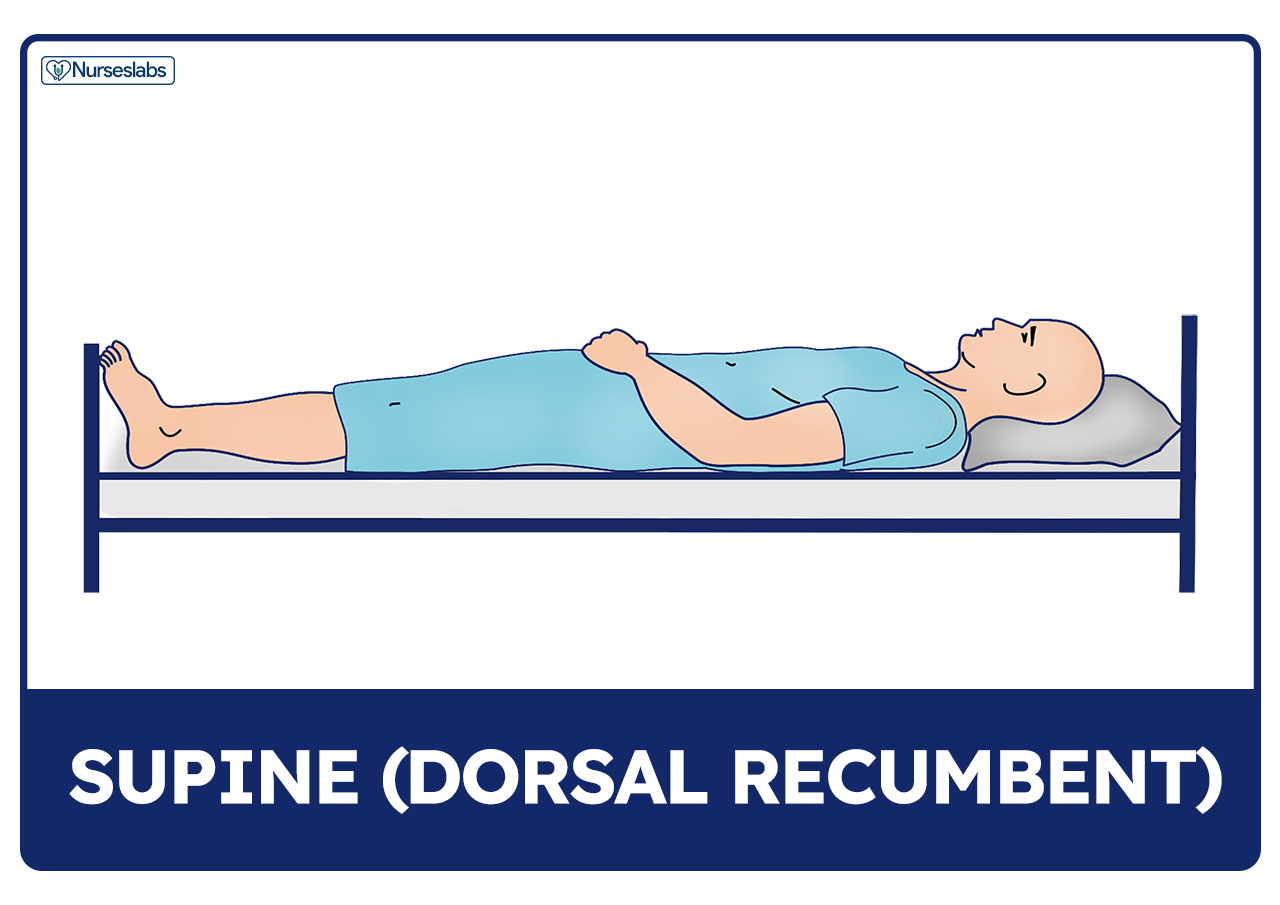


Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide



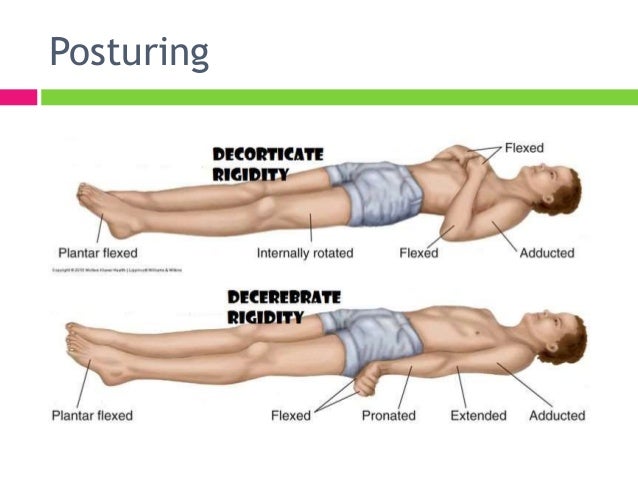
Abnormal Posturing Wikipedia


Diabetic Coma Symptoms And Causes Ausmed
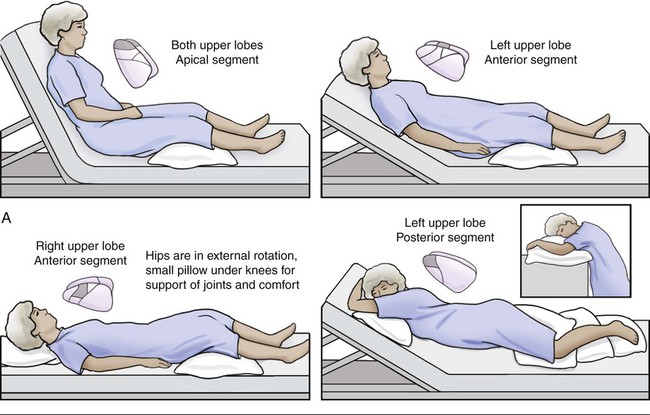


Airway Clearance Techniques Thoracic Key
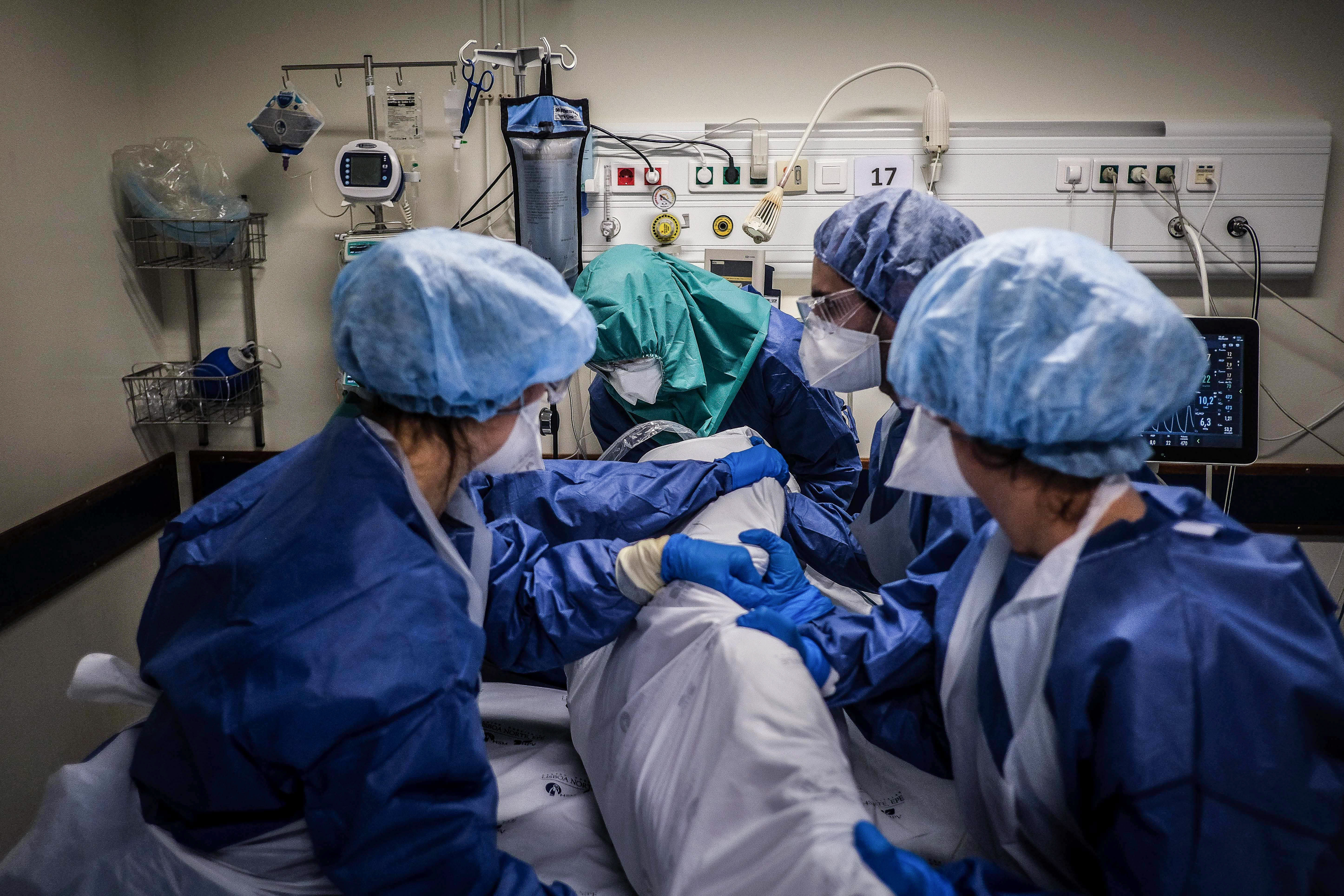


Icu Doctors Can Get Covid Patients Off Ventilators Faster The Washington Post



Forensic Nurses Helping Comatose Patients



Neurological Assessment Of Coma Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry


3 5 Positioning Patients In Bed Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient Care



Pdf Sitting Position Improves Consciousness Level In Patients With Cerebral Disorders
/GettyImages-594415972-0250a7e3d0264f2ca7e801449fd68795.jpg)


How To Recognize And Treat End Stage Death Rattle


3 6 Assisting A Patient To A Sitting Position And Ambulation Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient Care



1 428 Coma Patient Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images


Is The Supine Position Associated With Loss Of Airway Patency In Unconscious Trauma Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Scandinavian Journal Of Trauma Resuscitation And Emergency Medicine Full Text



Woman Shares Horrifying Photo Of Binge Drinking Coma To Warn Of Alcohol Dangers The Independent The Independent



Approach To The Comatose Patient



How To Perform Oral Care For Unconscious Patient In Hospital



Coma Wikipedia



Sleeping Positions What S The Best Sleeping Position
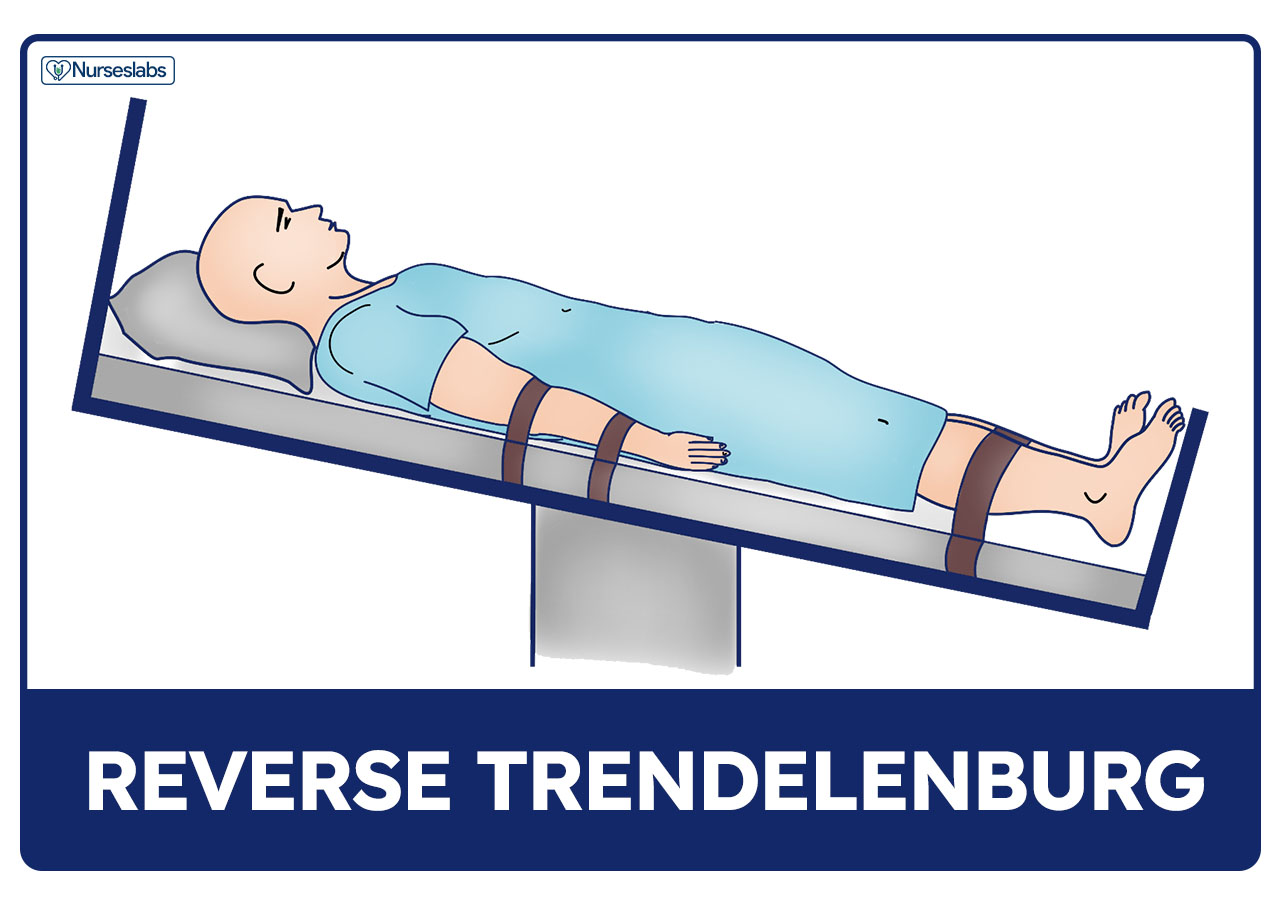


Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide


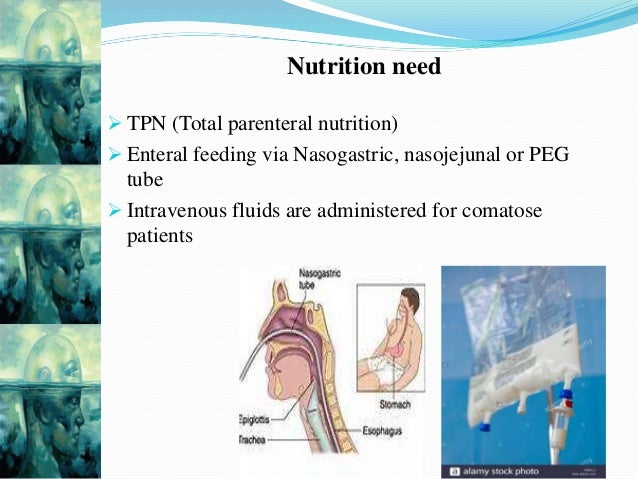
Nasogastric And Feeding Tube Placement Clinical Gate



Unconscious Oral Care Youtube



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿